RDF Graph Model
Contents
[hide]RDF Graph Model
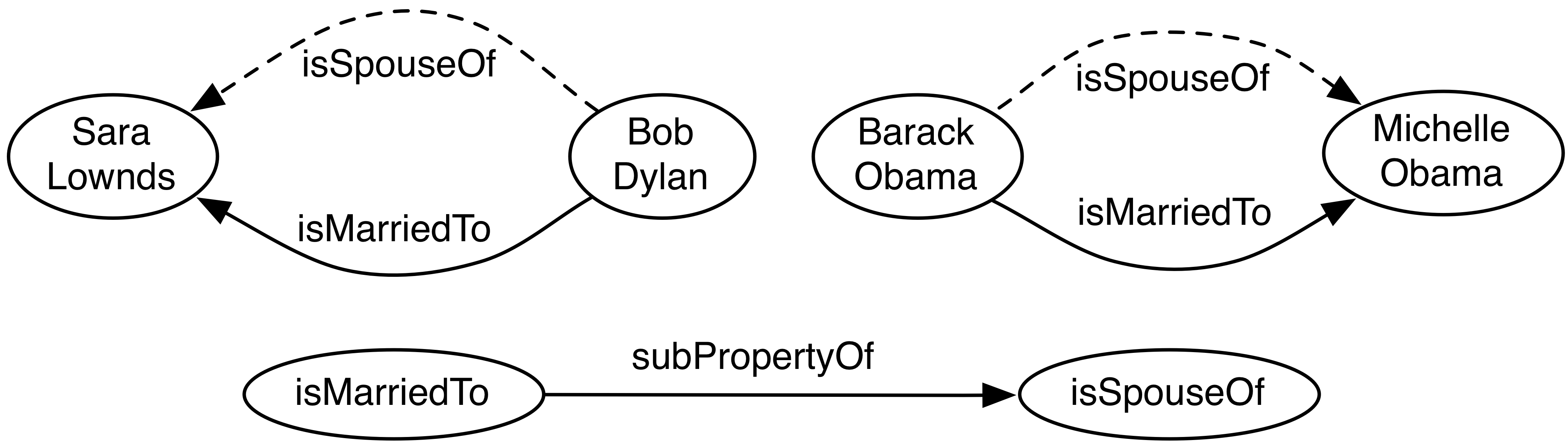
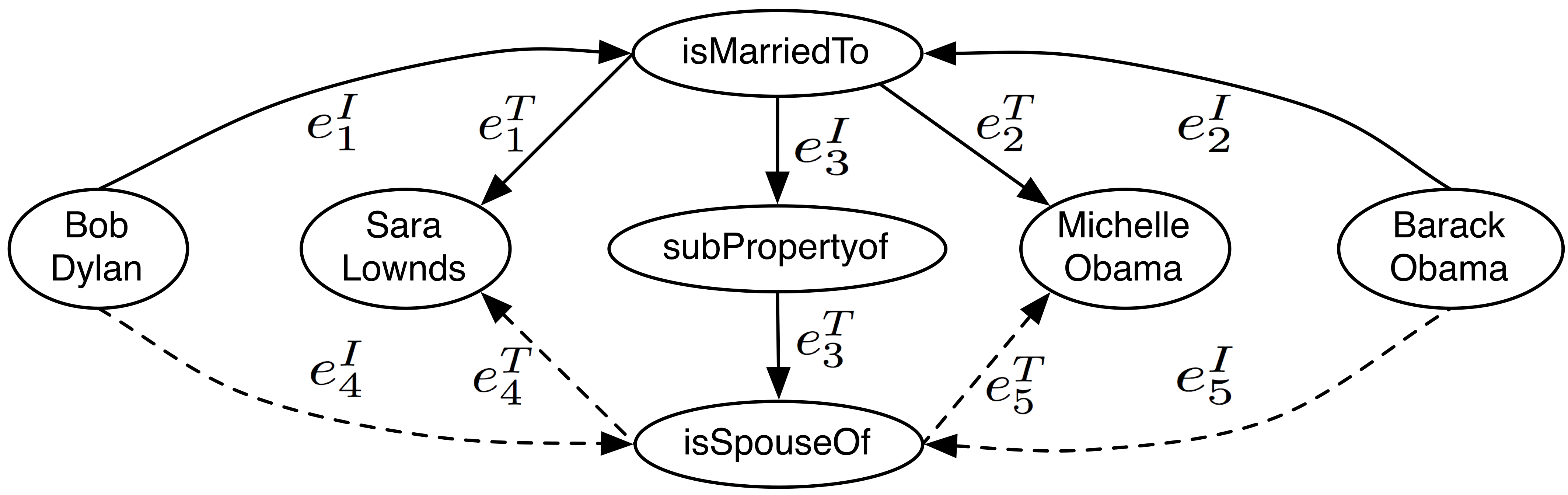
We propose a new formal model for representing any set of RDF triples as a labeled directed multigraph, or LDM. Two existing approaches use either Node-LabeledArc-Node (NLAN) diagram or Bipartite (BI) graph. We demonstrate the three approaches using the following example.
Example
| Triple | Subject | Predicate | Object |
|---|---|---|---|
| T1 | BobDylan | isMarriedTo | SaraLownds |
| T2 | BarackObama | isMarriedTo | MichelleObama |
| T3 | isMarriedTo | rdfs:subPropertyOf | isSpouseOf |
| T4 | BobDylan | isSpouseOf | SaraLownds |
| T5 | BarackObama | isSpouseOf | MichelleObama |
For the set of RDF triples in the table above, we explain how each approach represents them in the graph.
The NLAN model
The BI model
The LDM model
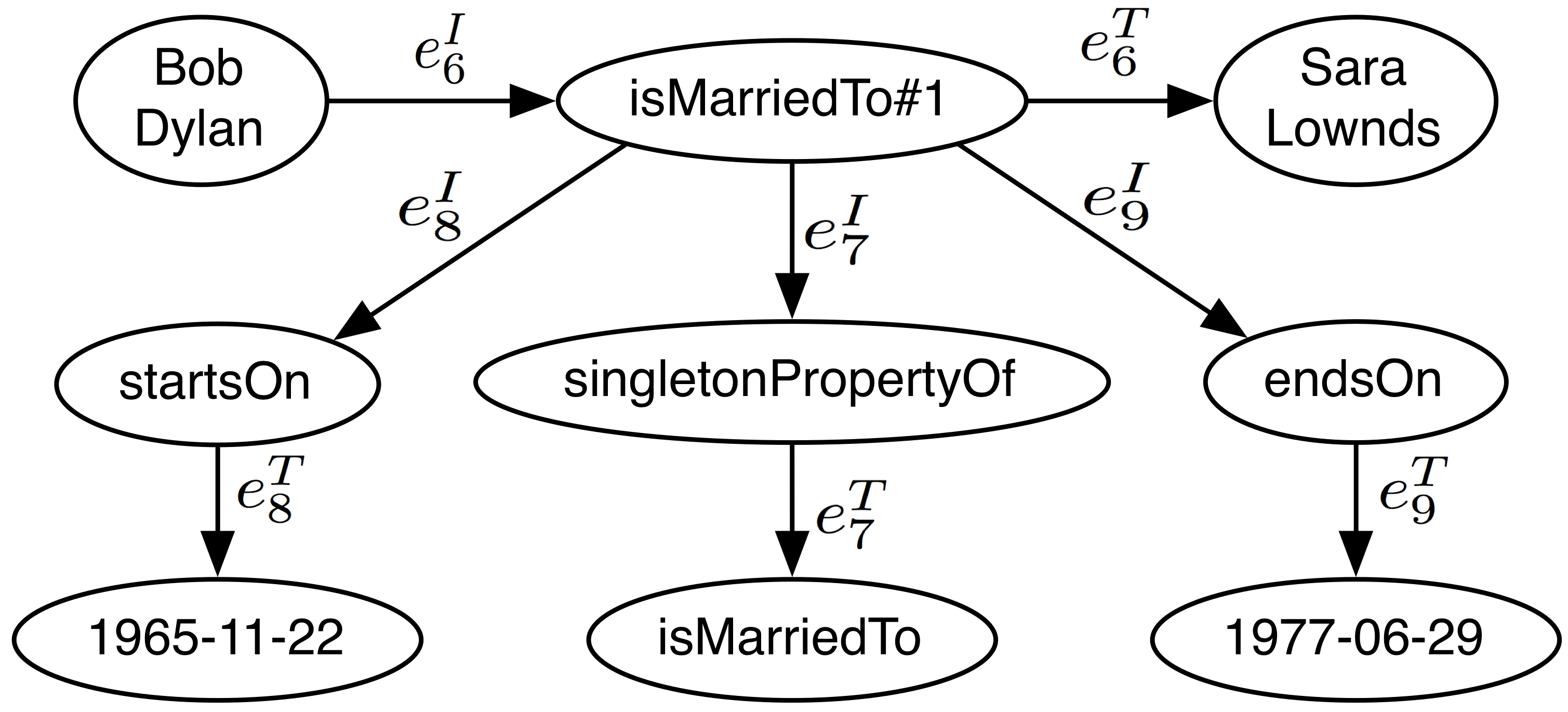
More complex examples
We use Singleton_Property approach to represent the duration of the marriage between Bob Dylan and Sara Lownds.
Empirical studies
RDF Datasets
We use four RDF datasets that are publicly available on the Web.
- BKR-SP: created by Vinh Nguyen et al. ACM. This dataset is available at Singleton_Property.
- YAGO2S-SP: also created by Vinh Nguyen et al. ACM. This dataset is also available at Singleton_Property
- DBPedia 3.9: download at DBPedia39
- Freebase: download at Freebase. For our experiment, we downloaded this dataset on March 30.
Experimental Result Files
We created multiple MapReduce jobs to compute the degree distributions of all three approaches on four RDF datasets.
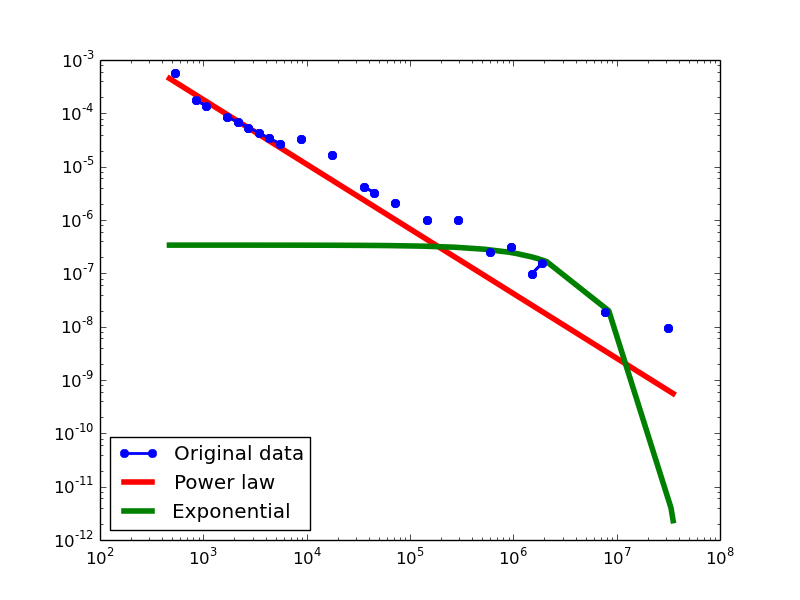
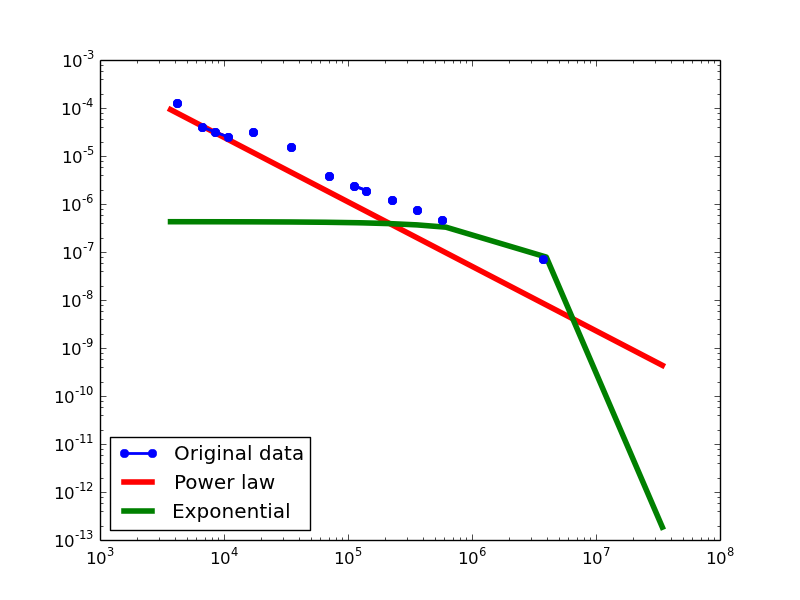
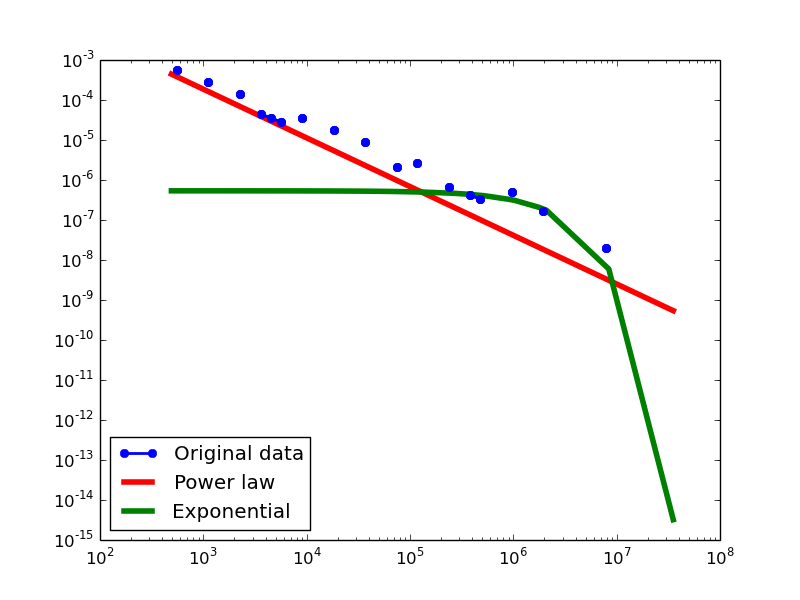
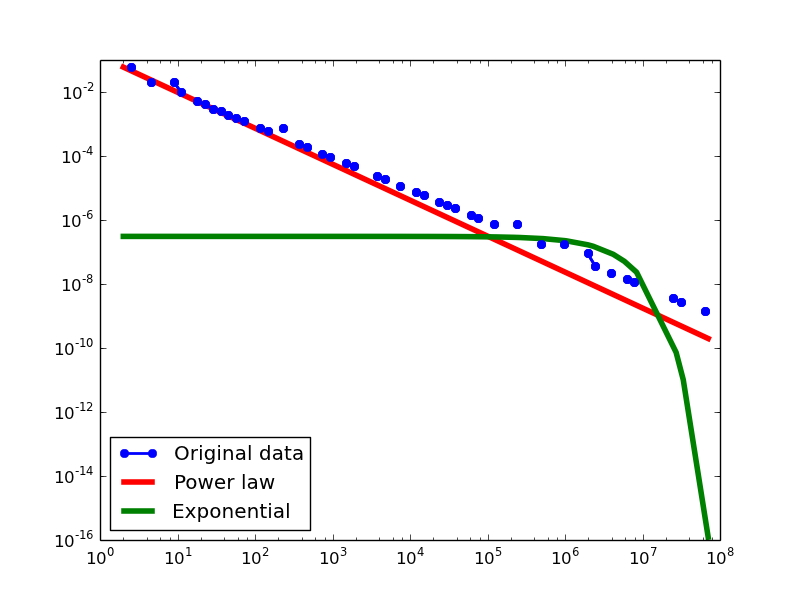
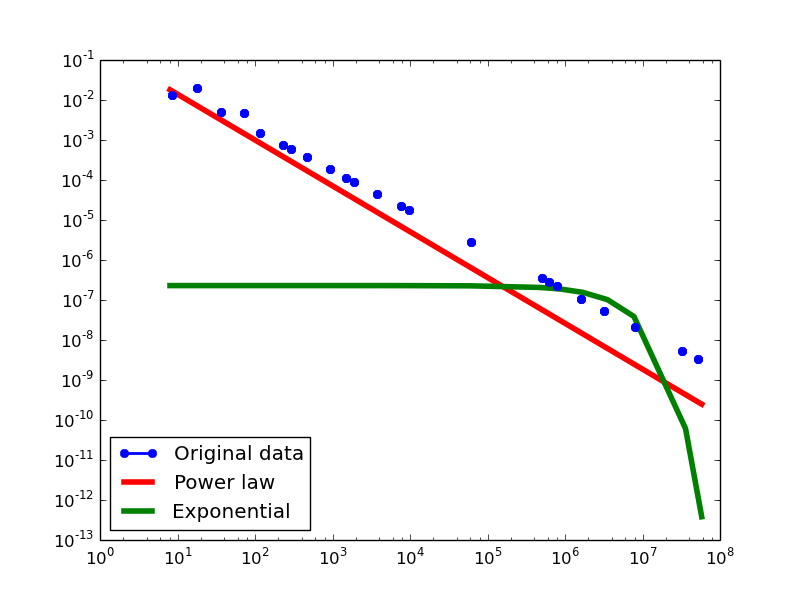
Plotting Degree distributions
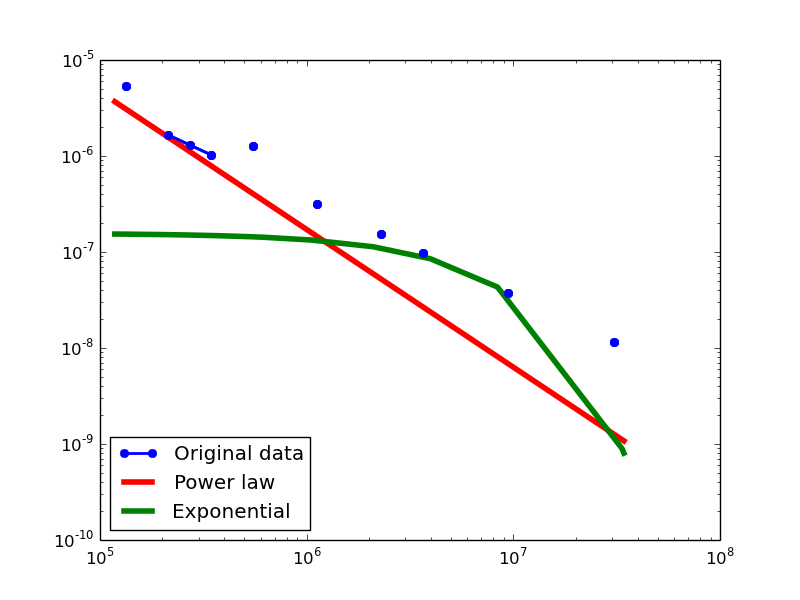
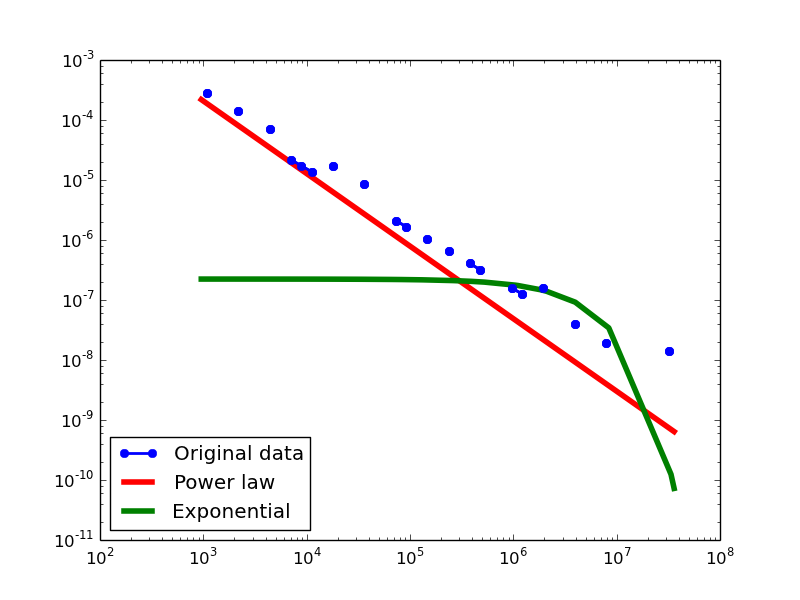
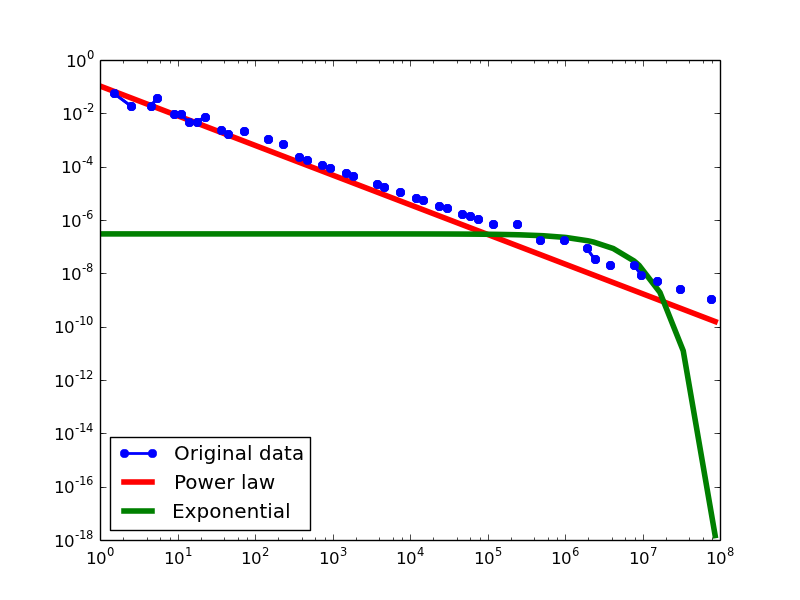
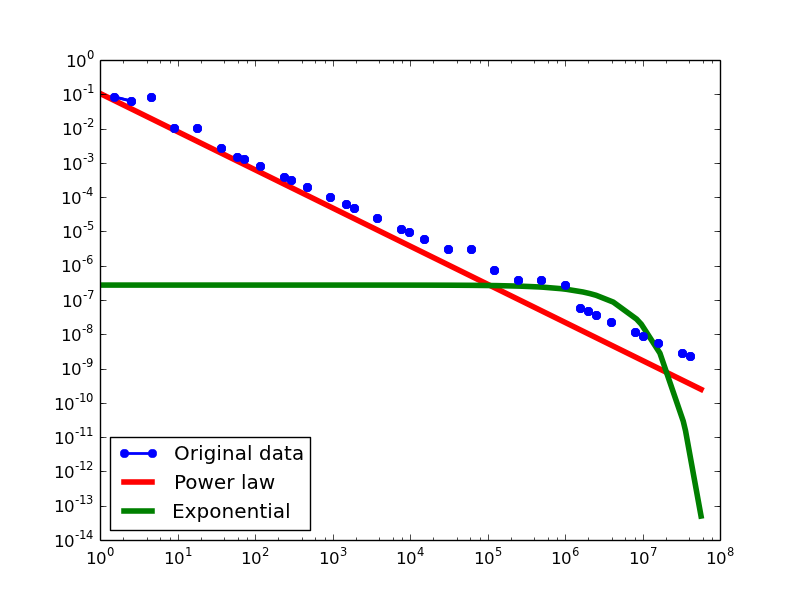
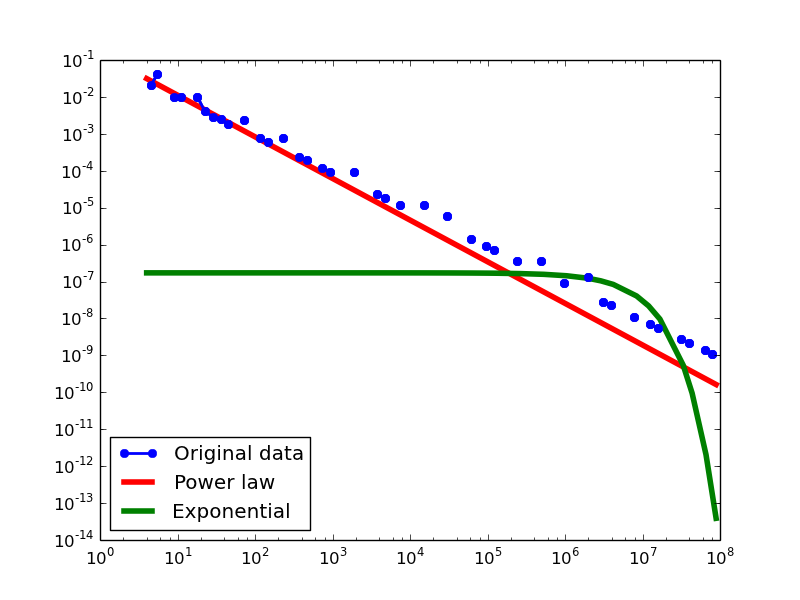
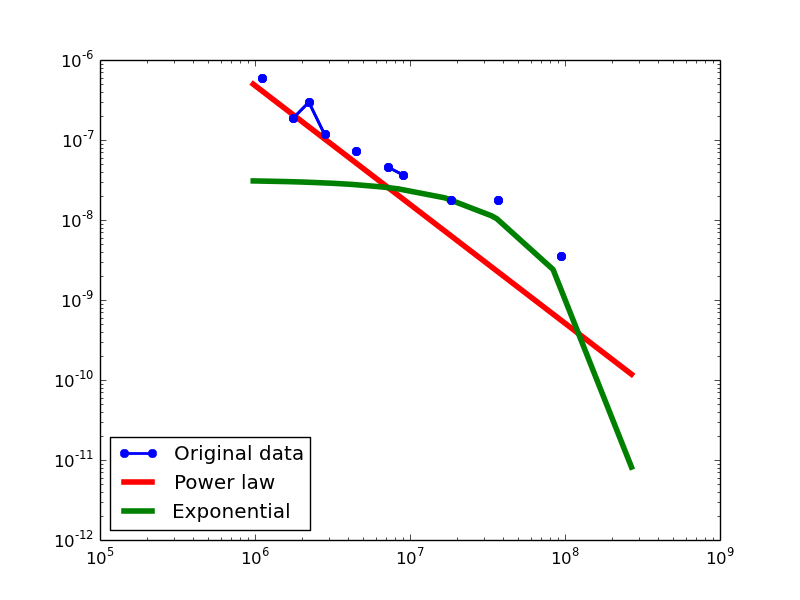
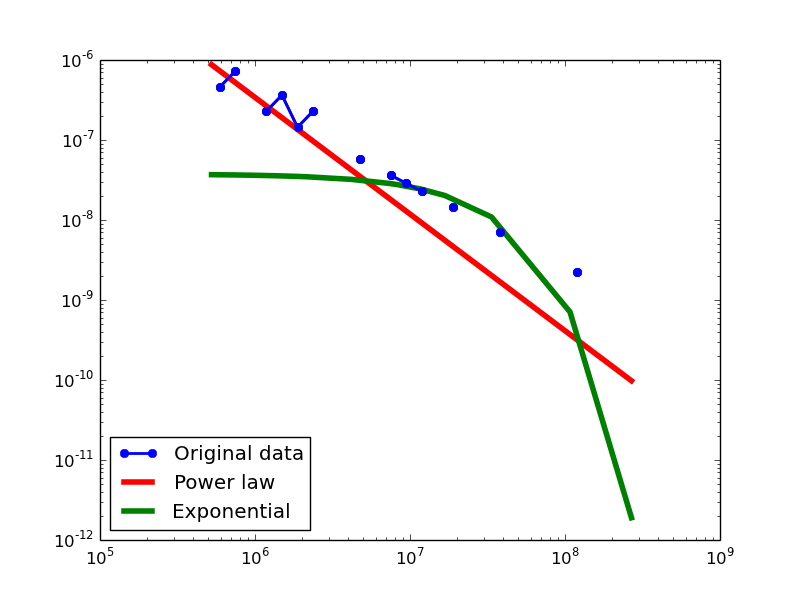
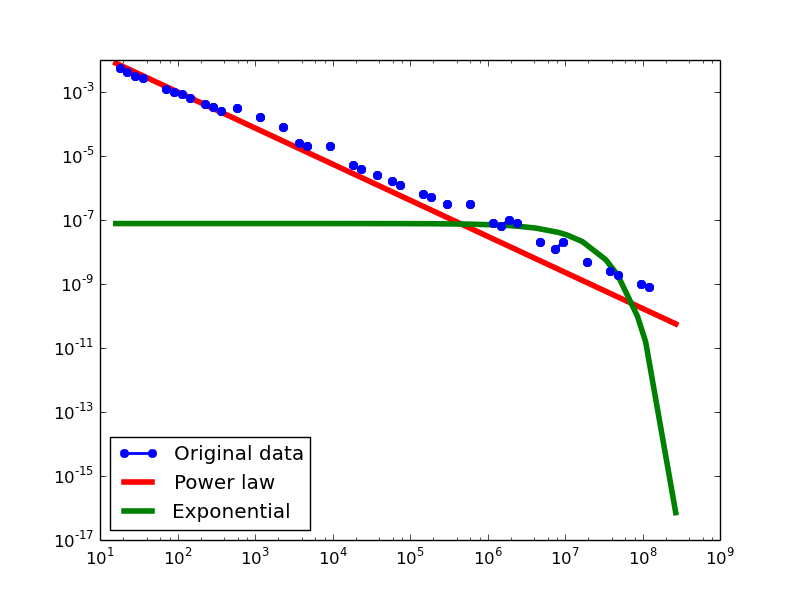
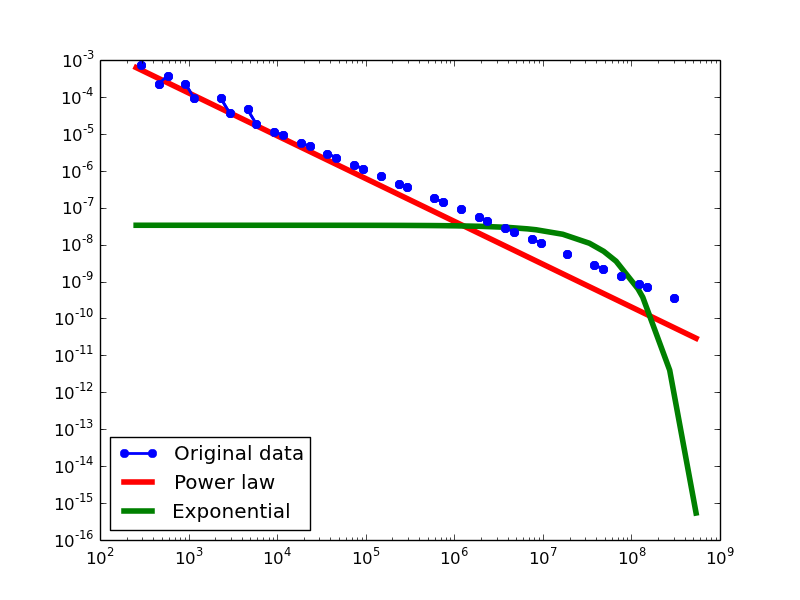
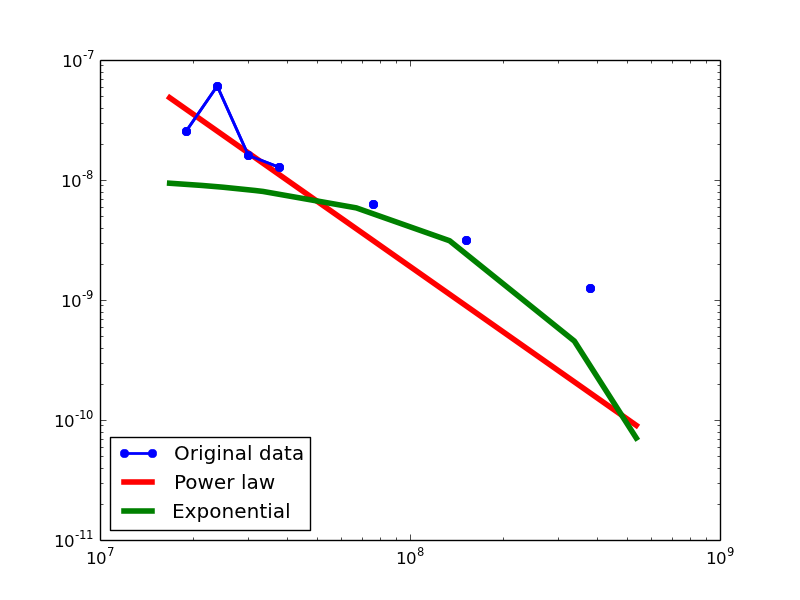
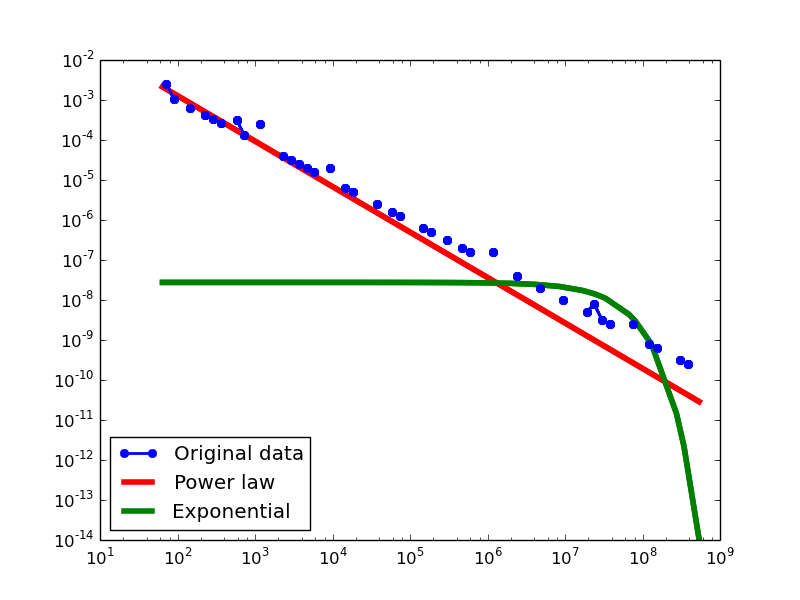
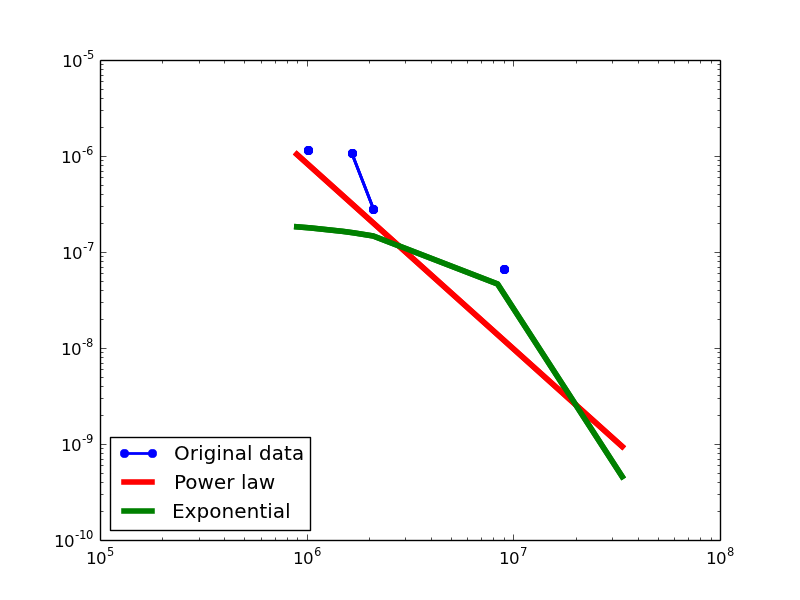
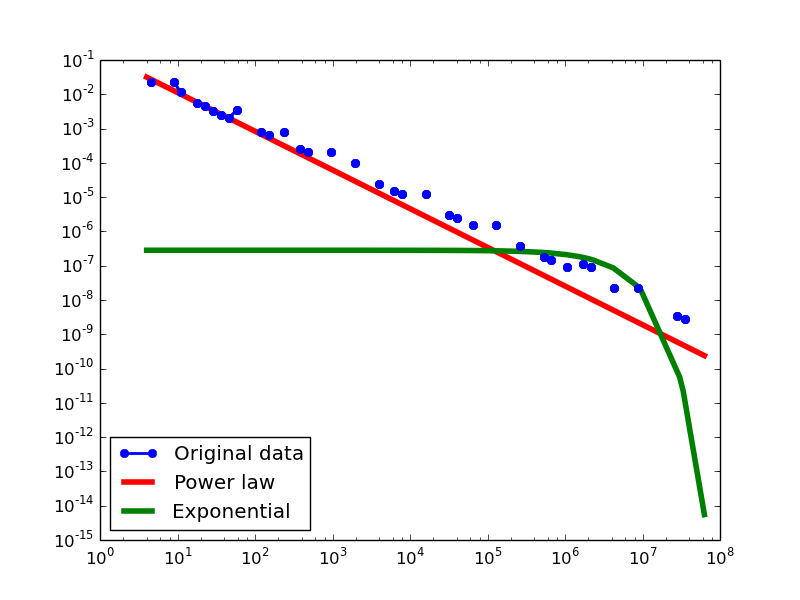
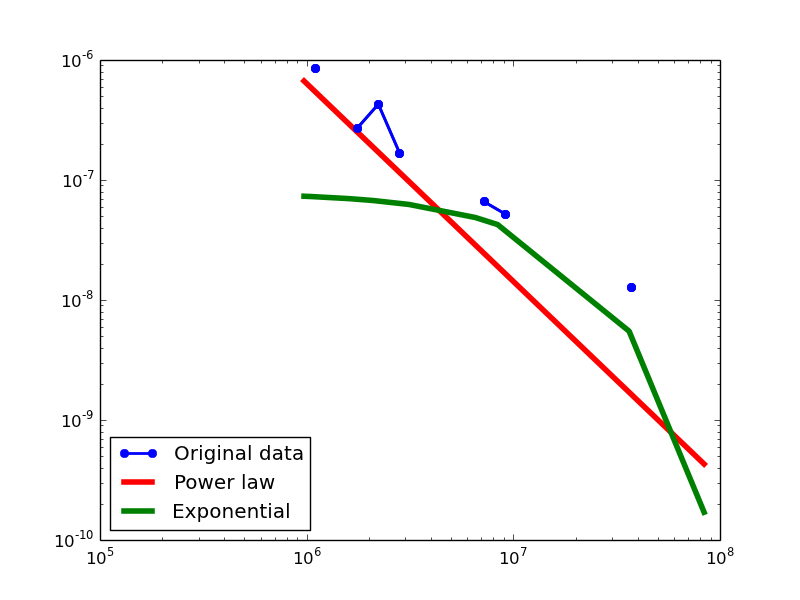
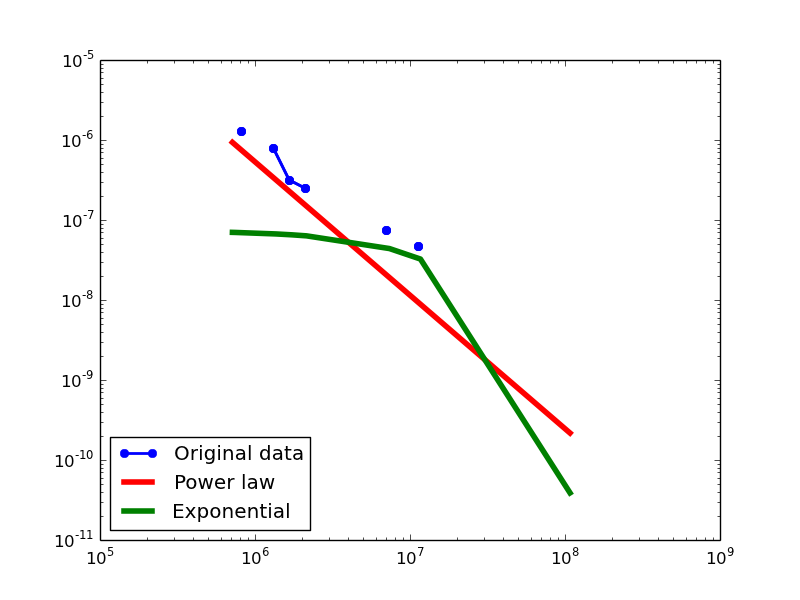
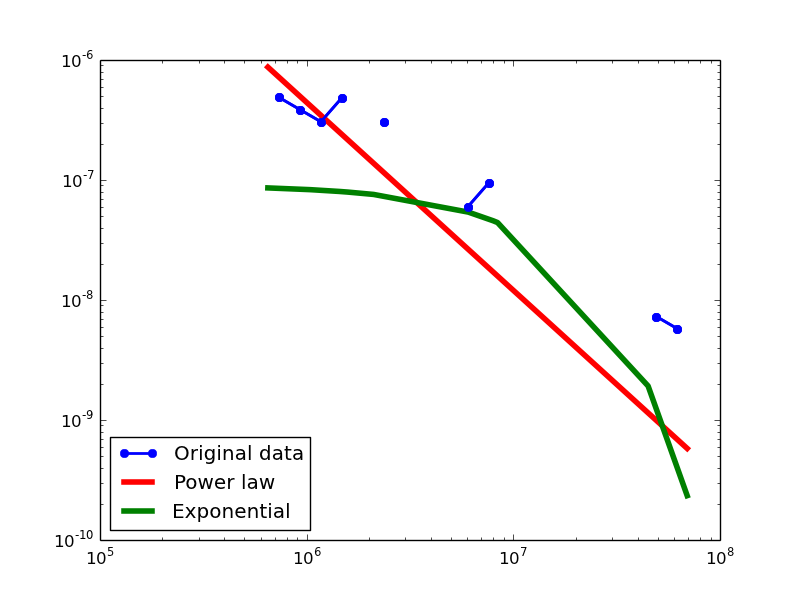
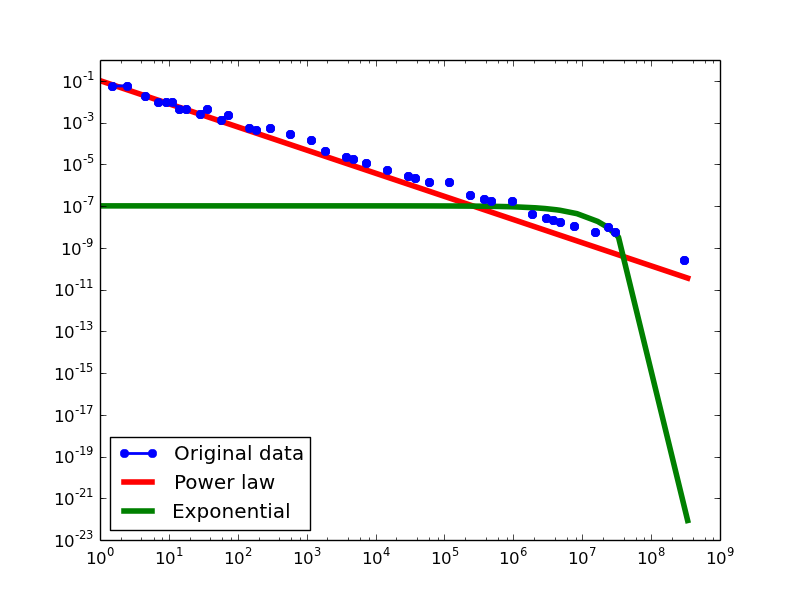
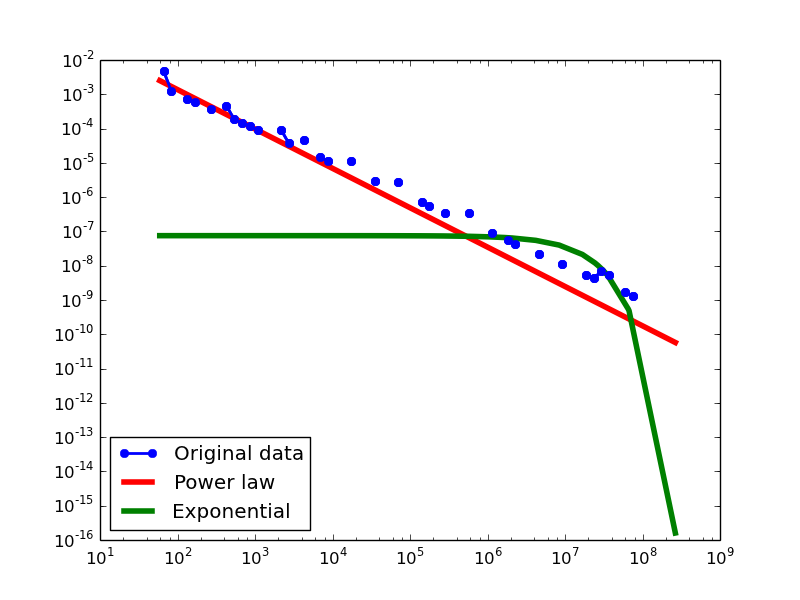
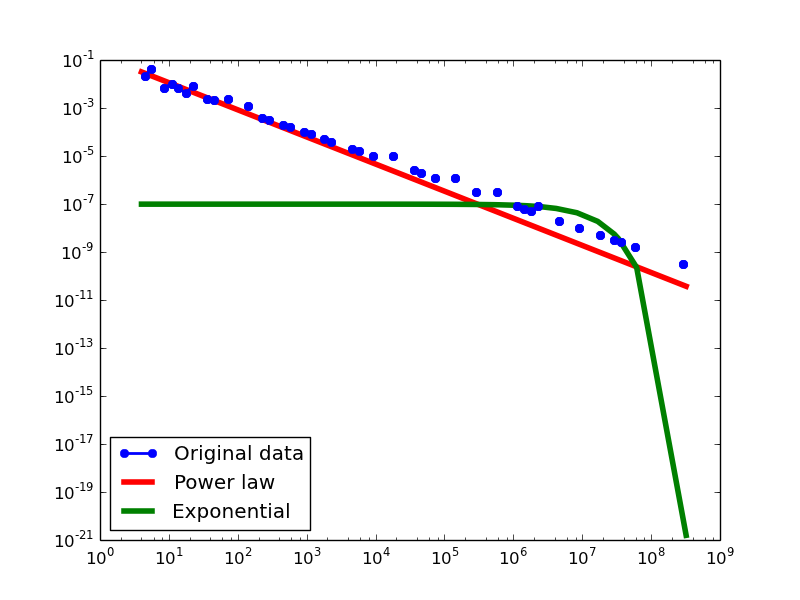
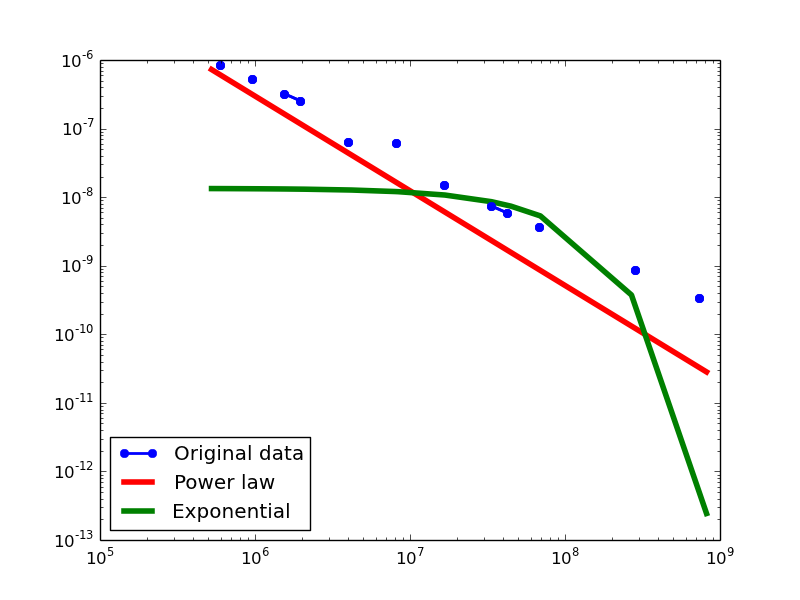
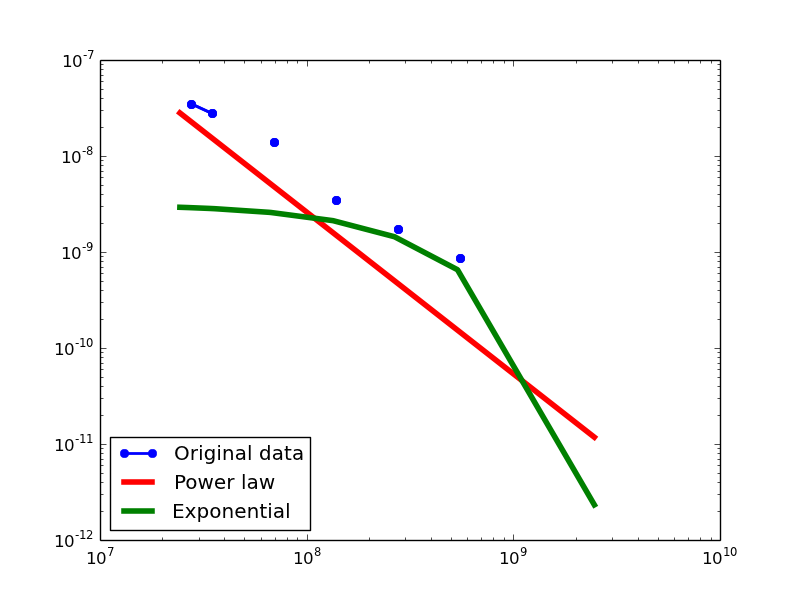
Here we plot the degree distributions of three approaches (LDM, NLAN, BI) on four RDF datasets.
For each dataset, we compute in-degree, out-degree, and total-degree distributions for LDM and NLAN approaches. BI approach has only total-degree distribution because it is undirected graph. We also compare the power law fit vs. exponential fit for each plot.
LDM
| DS | Degree type | alpha | xmin | sigma | R | p | D min | Tail coverage |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BKR | in | 1.12 | 1 | 0.02 | 6.78 | 1.24E-11 | 0.15 | 60% |
| out | 1.23 | 1024 | 0.04 | 4.01 | 6.10E-05 | 0.14 | 28% | |
| total | 1.21 | 955 | 0.04 | 3.95 | 7.87E-05 | 0.13 | 58.33% | |
| YAGO2S | in | 1.11 | 1 | 0.02 | 6.33 | 2.52E-10 | 0.14 | 96.3% |
| out | 1.11 | 1 | 0.02 | 5.98 | 2.18E-09 | 0.14 | 96.3% | |
| total | 1.13 | 4 | 0.02 | 6.36 | 2.03E-10 | 0.12 | 92.31% | |
| DBPEDIA | in | 1.49 | 974383 | 0.13 | 1.76 | 0.08 | 0.11 | 25% |
| out | 1.46 | 524288 | 0.11 | 2.47 | 0.01 | 0.12 | 28.57% | |
| total | 1.13 | 16 | 0.02 | 5.38 | 7.39E-08 | 0.15 | 85.19% | |
| FREEBASE | in | 1.16 | 256 | 0.02 | 5.56 | 2.65E-08 | 0.11 | 70% |
| out | 1.81 | 16777216 | 0.26 | 1.54 | 0.12 | 0.12 | 16.67% | |
| total | 1.14 | 64 | 0.02 | 5.91 | 3.51E-09 | 0.12 | 79.31% |
BKR-SP
- LDM graphs transformed from the BKR-SP dataset
YAGO2S-SP
- LDM graphs transformed from the YAGO2S-SP dataset
DBPEDIA
- LDM graphs transformed from the DBPedia dataset
FREEBASE
- LDM graphs transformed from the Freebase dataset
NLAN
This table shows the parameters of the best power law distributions for each datasets using the NLAN approach.
| Dataset | Type | alpha | xmin | Dmin | sigma | R | p | Tail Coverage |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BKR-SP | in | 1.933211288 | 895825 | 0.127628625 | 0.329940015 | 2.271051161 | 0.023143881 | 12.5% |
| out | 1.343236826 | 3705 | 0.115026299 | 0.083247158 | 3.894424558 | 9.84E-05 | 31.58% | |
| total | 1.21774704 | 491 | 0.141337886 | 0.041150323 | 3.228857504 | 0.001242858 | 58.33% | |
| YAGO2S-SP | in | 1.123959864 | 2 | 0.13926462 | 0.017708552 | 6.236336995 | 4.48E-10 | 92.31% |
| out | 1.145682633 | 8 | 0.12183686 | 0.029136527 | 4.997441147 | 5.81E-07 | 73.33% | |
| total | 1.128566546 | 4 | 0.132747188 | 0.019165569 | 5.732859944 | 9.88E-09 | 84.62% | |
| DBPEDIA | in | 1.648887842 | 970956 | 0.10993169 | 0.205196353 | 1.899457176 | 0.057504392 | 12.5% |
| out | 1.668078604 | 715028 | 0.128189532 | 0.222692868 | 2.574136552 | 0.01004906 | 0% | |
| total | 1.566221177 | 649090 | 0.147983393 | 0.163453975 | 1.774194648 | 0.076030959 | 12.5% | |
| FREEBASE | in | 1.176440054 | 410 | 0.117914742 | 0.028622356 | 4.937155187 | 7.93E-07 | 64.29% |
| out | 1.10925354 | 1 | 0.119199458 | 0.015007128 | 6.185548611 | 6.19E-10 | 96.3% | |
| total | 1.148300227 | 59 | 0.123663745 | 0.0223571 | 5.311427686 | 1.09E-07 | 77.78% |
BKR-SP
- NLAN graphs transformed from the BKR-SP dataset
YAGO2S-SP
- NLAN graphs transformed from the YAGO2S-SP dataset
DBPEDIA
- NLAN graphs transformed from the DBPedia dataset
FREEBASE
- NLAN graphs transformed from the Freebase dataset
BI
This table shows the parameters of the best power law distributions for each datasets using the BI approach.
| Dataset | alpha | xmin | Dmin | sigma | R | p | Tail Coverage |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BKR | 1.201698959 | 491 | 0.127904446 | 0.037454556 | 4.762452101 | 1.91E-06 | 62.5% |
| Yago2s | 1.129751796 | 4 | 0.124153477 | 0.018728059 | 6.136824765 | 8.42E-10 | 92.31% |
| DBpedia | 1.381014259 | 524288 | 0.116475129 | 0.092409531 | 2.766134059 | 0.005672521 | 26.93% |
| Freebase | 1.684343461 | 24352099 | 0.105289281 | 0.216408404 | 2.006340037 | 0.044819981 | 13.79% |
Degree Distribution
- BI graphs transformed from four datasets
Comparison
This table compares the power-law degree distribution of three type of graphs (NLAN, LDM, and BI) based on four RDF datasets (BKR, YAGO2S, DBPEDIA and FREEBASE. The values are the percentage of data points in each degree distribution that are covered by the power law. Distribution with higher percentage will better reflect power law distribution in the tail.
| DS | degree | NLAN | LDM | BI |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BKR | in | 12.5% | 60% | NA |
| out | 31.58% | 28% | NA | |
| total | 58.33% | 58.33% | 62.5% | |
| YAGO2S | in | 92.31% | 96.3% | NA |
| out | 73.33% | 96.3% | NA | |
| total | 84.62% | 92.31% | 92.31% | |
| DBPEDIA | in | 12.5% | 25% | NA |
| out | 0% | 28.57% | NA | |
| total | 12.5% | 85.19% | 29.63% | |
| FREEBASE | in | 64.29% | 70% | NA |
| out | 96.3% | 16.67% | NA | |
| total | 77.78% | 79.31% | 13.79 |
LDM and NLAN
In general, LDM distributions have higher coverage percentage than the NLAN graphs. Out of 12 degree distributions, 9 LDM distributions have higher coverage than NLAN distributions while only 2 NLAN distributions have higher percentage. Both share the same coverage for BKR total degree distribution. Especially for all the in-degree and total-degree distributions, 100% LDM distributions have higher percentage than the NLAN distributions.
LDM and BI
2 out of 4 LDM graphs have significantly higher coverage percentage than the BI graphs, particularly in the total degree distributions of DBPedia (LDM: 85.19% vs. BI: 29.63%) and Freebase (LDM: 79.31% vs. BI: 13.79%).