Twitris
Twitris, a Semantic Web application that facilitates understanding of social perceptions by Semantics-based processing of massive amounts of event-centric data. Twitris 2.0 addresses challenges in large scale processing of social data, preserving spatio-temporal-thematic properties. Twitris 2.0 also covers context based semantic integration of multiple Web resources and expose semantically enriched social data to the public domain. Semantic Web technologies enable the system's integration and analysis abilities.
Introduction
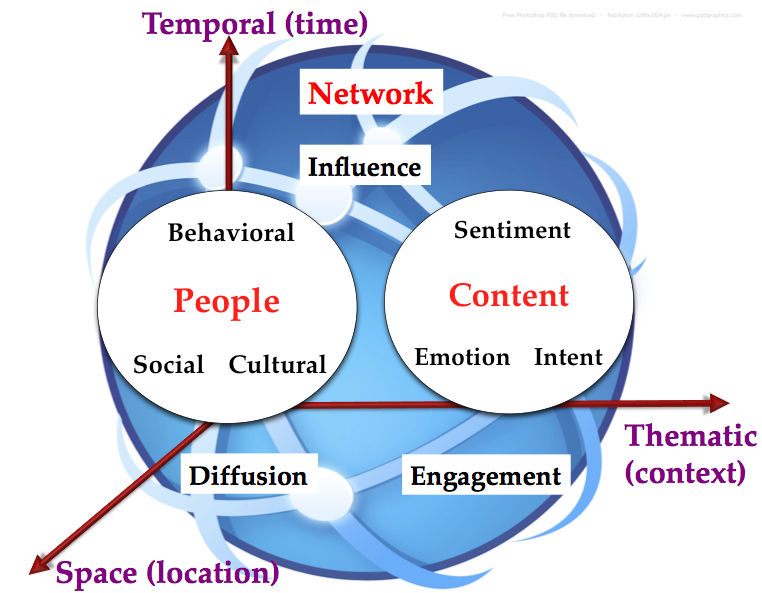
Well over a billion people have become 'citizens' of an Internet- or Web-enabled social community. Web 2.0 fostered the open environment and applications for tagging, blogging, wikis, and social networking sites that have made information consumption, production, and sharing so incredibly easy. With over 5 billion mobile connections, over a billion with data connections (smartphones) and with many more having ability to communicate using SMS, digital media can be shared with the rest of the humanity instantly. As a result, humanity is interconnected as never before. This interconnected network of people actively observe, report, collect, analyze, and disseminate information via text, audio, or video messages, increasingly through pervasively connected mobile devices, has led to what we term citizen sensing (Sheth, 2009-a) (Sheth, 2009-b). This phenomenon is different from the traditional centralized information dissemination and consumption environments where citizens primarily act as consumers of reported information from several authoritative sources. This citizen sensing is complemented by the growing ability to access, integrate, dissect, and analyze individual and collective thinking of humanity, giving us a capability that is recognized as collective intelligence. Citizen sensing involves humans in the loop, and with it all the complexities associated with and intelligence captured in human communication. As citizen sensing has gained momentum, it’s generating millions of observations, creating significant information overload. In many cases it becomes nearly impossible to make sense of the information around a topic of interest. Given this data deluge, analyzing the numerous social signals can be extremely challenging. In response to this growing citizen sensing data deluge, Twitris has been developed with the vision of performing semantics-empowered analysis of a broad variety of social media exchanges. Twitris, named by combining Twitter with Tetris, a tile-matching puzzle game, has incorporated increasingly sophisticated analysis of social data and associated metadata, combining it with background knowledge, and more recently (albeit not discussed here) machine sensor or data captured from sensors and devices that make up Internet of Things (IoT). Twitris’ evolution can be characterized in three phases (and corresponding versions of the system). Figure 1 outlines the corresponding dimensions Twitris considers.
What is Twitris?
In response to this growing data deluge, we have developed Twitris (currently Twitris 2.0) with the vision of performing semantics-empowered analysis of a broad variety of social media content. Specifically, Twitris aims to capture semantics (i.e., meaning and understanding) with spatial, temporal, thematic dimensions, user intentions and sentiments, networking behavior (user interactions patterns and features such as information diffusion and centrality) and other information present in social media. Semantic Web technologies enable its core integration, analysis and data/knowledge sharing abilities. Twitris 2.0, focuses only on content centric analysis , leveraging the relevant Semantic Web technologies, background knowledge, languages, tools where appropriate.
Twitris 2.0 is a Semantic Social Web approach to detect social signals by analyzing massive, event-centric data through:
- Analysis of casual text with spatio-temporal-thematic (STT) bias, to extract event descriptors.
- Capturing semantics from contexts associated with tweets.
- Use of deep semantics (using automatically created domain models) to understand the meaning of standard event descriptors.
- Use of shallow semantics(semantically annotated entities) for knowledge discovery and representation.
- Exposure of processed social data to the public domain, complying with semantic Web standards.
- Semantic Integration of multiple external Web resources (news, articles, images and videos) utilizing the semantic similarity between contexts.
Twitris 2.0 is developed as a multi-layered system where each component acts as part of a pipeline. The system is currently being used for a number of People-Content-Network study experiments and being extended to integrate with SMS and other Web data used by a number of widely deployed open source projects. These include applications used by non governmental organizations (NGO) in developing countries for crisis management (in particular, Ushahidi.org, eMoksha.org and Kiirti.org). Twitris 2.0 is being extended with Twarql technology for limited real-time support and is being adapted for a cloud platform for much higher scalability.
COMING SOON... Twitris currently performs the Spatial, Temporal and Thematic analysis of the currently popular content on Twitter and so, does answer what is popular. Our current work focuses on analyzing Why and How that content is popular. We address the challenges of finding those elements of content and network properties, which contributes in this information diffusion / virality of the content.
TWITRIS is part of a larger research agenda on semantics-enriched social computing [1, 2, 4] at the Ohio Center of Excellence in Knowledge-Enabled Computing (Kno.e.sis) Center at the Wright State University, Dayton, Ohio (other key themes include semantics-enriched services computing and the sensor Web).
Twitris as you see is a work in progress, but is rapidly maturing. Technical details can be found in [3]. Data aggregation/cleaning, text processing/analysis etc. are highly compute intensive tasks. Following the "Health Care Reform" that we analyzed on a state wide basis for the US, we will next introduce "Iran Elections" which will provide global country wide assessment of social signals. As of now, our system hosts analysis up until a week prior to the current date and we intend to reduce this period. Analysis of real-time data for more events will be added as time permits.
Publications
- A. Jadhav et al., Twitris 2.0 : Semantically Empowered System for Understanding Perceptions From Social Data, ISWC Semantic Web Challenge 2010.
- A. Sheth, Semantic Integration of Citizen Sensor Data and Multilevel Sensing: A comprehensive path towards event monitoring and situational awareness, February 17, 2009.
- A. Sheth, Citizen Sensing, Social Signals, and Enriching Human Experience IEEE Internet Computing, July/August 2009.
- M. Nagarajan et al., Spatio-Temporal-Thematic Analysis of Citizen-Sensor Data - Challenges and Experiences, Tenth International Conference on Web Information Systems Engineering, Oct 5-7, 2009, Poland.
- What are people talking about, Why people write, How people write: Meena Nagarajan's research
- Real Time Web - A primer Part I and Part II, August 29, 2009
Internal
For project members only: Twitris Internal Page