Difference between revisions of "Twarql Continuous Semantics"
(→Introduction) |
(→Introduction) |
||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
The recent years have seen a significant change in the dissemination of news and information. Observations of unfolding events are increasingly shared real-time through ubiquitously accessible microblogging platforms. However, the information being shared is growing exponentially. Twitter alone generates more than 100 Million microposts a day. This avalanche of data makes it difficult to seek out specific information, especially when done real-time. Event-specific information is often only temporarily interesting and gets stale quickly. To achieve the highest information gain it is important that select content finds its way to the user quickly. This kind of information tracking has proved its importance in the recent Egypt protests where twitter and other social networking sites were used as major platforms for protesters to organize gatherings and to stay updated with major changes in the event. This paper presents a semantic web approach to support dynamic event tracking on twitter. | The recent years have seen a significant change in the dissemination of news and information. Observations of unfolding events are increasingly shared real-time through ubiquitously accessible microblogging platforms. However, the information being shared is growing exponentially. Twitter alone generates more than 100 Million microposts a day. This avalanche of data makes it difficult to seek out specific information, especially when done real-time. Event-specific information is often only temporarily interesting and gets stale quickly. To achieve the highest information gain it is important that select content finds its way to the user quickly. This kind of information tracking has proved its importance in the recent Egypt protests where twitter and other social networking sites were used as major platforms for protesters to organize gatherings and to stay updated with major changes in the event. This paper presents a semantic web approach to support dynamic event tracking on twitter. | ||
| − | In this work we offer a solution to the problem of event following based on the dynamic creation of semantic event models. The user will need to specify his area of interest only once, when an event model is automatically created. As the event unfolds, microposts are analyzed and, based on new developments, an updated model is created that subsequently filters microposts for the next iteration in the cycle. This work thus presents an early realization of [Continuous Semantics]. | + | In this work we offer a solution to the problem of event following based on the dynamic creation of semantic event models. The user will need to specify his area of interest only once, when an event model is automatically created. As the event unfolds, microposts are analyzed and, based on new developments, an updated model is created that subsequently filters microposts for the next iteration in the cycle. This work thus presents an early realization of [http://wiki.knoesis.org/index.php/Continuous_Semantics_to_Analyze_Real_Time_Data Continuous Semantics]. |
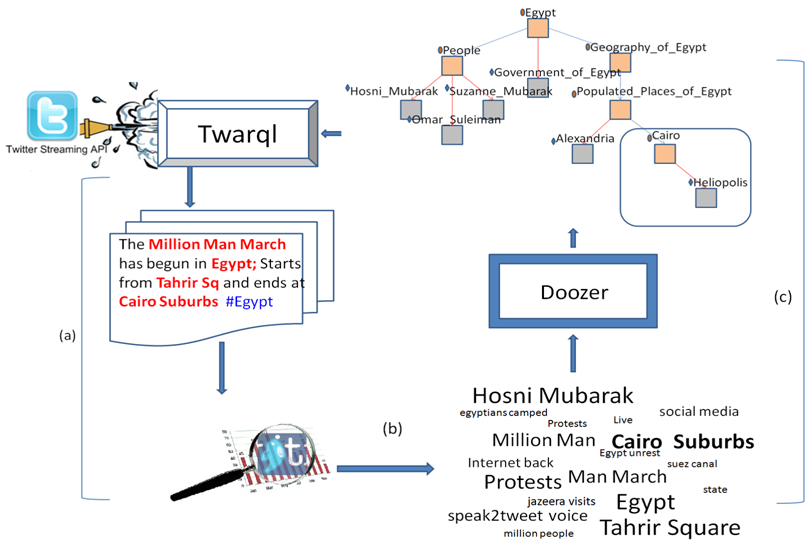
=Architecture and Approach= | =Architecture and Approach= | ||
Revision as of 16:22, 6 April 2011
Introduction
The recent years have seen a significant change in the dissemination of news and information. Observations of unfolding events are increasingly shared real-time through ubiquitously accessible microblogging platforms. However, the information being shared is growing exponentially. Twitter alone generates more than 100 Million microposts a day. This avalanche of data makes it difficult to seek out specific information, especially when done real-time. Event-specific information is often only temporarily interesting and gets stale quickly. To achieve the highest information gain it is important that select content finds its way to the user quickly. This kind of information tracking has proved its importance in the recent Egypt protests where twitter and other social networking sites were used as major platforms for protesters to organize gatherings and to stay updated with major changes in the event. This paper presents a semantic web approach to support dynamic event tracking on twitter.
In this work we offer a solution to the problem of event following based on the dynamic creation of semantic event models. The user will need to specify his area of interest only once, when an event model is automatically created. As the event unfolds, microposts are analyzed and, based on new developments, an updated model is created that subsequently filters microposts for the next iteration in the cycle. This work thus presents an early realization of Continuous Semantics.
Architecture and Approach
People
Pavan Kapanipathi
Christopher Thomas
Pablo Mendes
Amit Sheth