Difference between revisions of "Swapnil Soni Thesis"
| Line 25: | Line 25: | ||
[[File:Architecture_shs.png|center|thumb|650px|Architecture]] | [[File:Architecture_shs.png|center|thumb|650px|Architecture]] | ||
==Processing Pipeline== | ==Processing Pipeline== | ||
| − | We have used tweets (messages shared on Twitter) and URLs’ content (for URL mentioned in the tweets) as the data sources to extract relevant information for based on a given user given query. To extract relevant and recent information from real-time data, the first challenge is to create infrastructure for collecting a real-time tweet and extract meta-data of a tweet. In Social Health Signal, we have used Apache Storm component to extract tweets using the public Twitter streaming API while also performing meta-data extraction. Apache storm is free, open source software, used for real-time, distributed computing. Spouts and Bolts are basic components in storm for real-time processing of data. Networks of spouts and bolts are packaged into a <nowiki>no ''topology''</nowiki>, which is submitted to storm cluster. A tweet has many features, such as <b>text</b>, <b>short_url</b>, <b>latitude or longitude</b>, <b>retweet_count</b>, etc. All these features can be useful for finding out useful information. To extract all theses features from tweets in real-time. This process is also known as a pre-processing analytic pipeline, because the extracted features and data help to pattern extraction module. | + | We have used tweets (messages shared on Twitter) and URLs’ content (for URL mentioned in the tweets) as the data sources to extract relevant information for based on a given user given query. To extract relevant and recent information from real-time data, the first challenge is to create infrastructure for collecting a real-time tweet and extract meta-data of a tweet. In Social Health Signal, we have used Apache Storm component to extract tweets using the public Twitter streaming API while also performing meta-data extraction. Apache storm is free, open source software, used for real-time, distributed computing. Spouts and Bolts are basic components in storm for real-time processing of data. Networks of <b>spouts</b> and <b>bolts</b> are packaged into a <nowiki>no ''topology''</nowiki>, which is submitted to storm cluster. A tweet has many features, such as <b>text</b>, <b>short_url</b>, <b>latitude or longitude</b>, <b>retweet_count</b>, etc. All these features can be useful for finding out useful information. To extract all theses features from tweets in real-time. This process is also known as a pre-processing analytic pipeline, because the extracted features and data help to pattern extraction module. |
* <b>Spout:</b> | * <b>Spout:</b> | ||
A spout use the Streaming API to crawl real-time tweets. | A spout use the Streaming API to crawl real-time tweets. | ||
* <b>Bolt:</b> | * <b>Bolt:</b> | ||
The bolts contain computation logics to perform feature extraction logic in real-time. The first bolt is a filter bolt to identify the language of a tweet and allow only English tweets. Once all computing bolts are finished, the final bolt will save the data into the database. | The bolts contain computation logics to perform feature extraction logic in real-time. The first bolt is a filter bolt to identify the language of a tweet and allow only English tweets. Once all computing bolts are finished, the final bolt will save the data into the database. | ||
Revision as of 22:36, 15 May 2015
Thesis title:
Domain Specific Document Retrieval Framework for Near Real-time Social Health Data.
Committees:
Mentor:
Introduction
With the advent of the web search and microblogging, the percentage of Online Health Information Seekers (OHIS) using these online services to share and seek health real-time information has increased exponentially. When OHIS turn to search engine or microblogging search services to seek out real-time information, the results are not promising. It is extremely difficult for users to retrieve relevant results based on query alone; they may get overwhelmed by the information overload. Following are the challenges exist in the current systems are:
- Results are limited to keyword based techniques to retrieve useful health information for a given query
- The results do not contain real-time information
- Microblogging search services use posts or messages to find out information (e.g, Twitter search engine uses tweet to get information)
- Ranking of results are based on relevancy
In our approach, we have considered Twitter to search documents based on some unique features: triple-pattern based mining, near real-time retrieval, tweet contained URL based search, and ranking based on popularity and relevancy of the results. First, triple based pattern (subject, predicate, and object) mining technique extracts triple patterns from microblog messages--related with chronic health conditions. The triple pattern is defined in the initial question. Second, in order to make the system near real-time, the search results are divided into intervals of six hours. Third, in addition to tweets, we use URLs’ (mentioned in the tweet) content as the data source. Finally, the results are ranked according to relevance and popularity such that at a particular time the most relevant information for the questions are displayed instead of only temporal relevance.
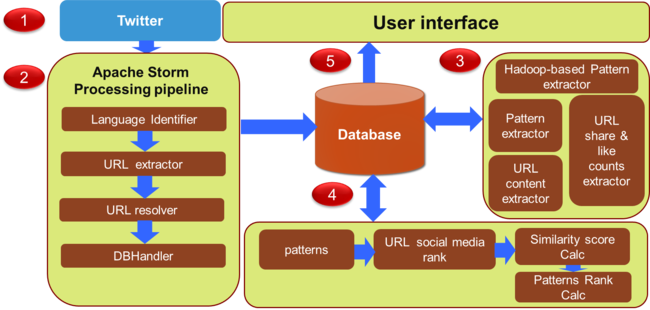
Architecture
Our platform (Social Health Signal) is based on a) large scale real-time Twitter data processing b) semantic web techniques and domain knowledge c) triple-pattern based text mining. The system is divided into three major components.
- Processing Pipeline: To collect and extract meta-data information from the tweets.
- Pattern Extractor: It extracts relevant documents related to a given query
- Rank Calculator: This module calculate the rank of the results
Processing Pipeline
We have used tweets (messages shared on Twitter) and URLs’ content (for URL mentioned in the tweets) as the data sources to extract relevant information for based on a given user given query. To extract relevant and recent information from real-time data, the first challenge is to create infrastructure for collecting a real-time tweet and extract meta-data of a tweet. In Social Health Signal, we have used Apache Storm component to extract tweets using the public Twitter streaming API while also performing meta-data extraction. Apache storm is free, open source software, used for real-time, distributed computing. Spouts and Bolts are basic components in storm for real-time processing of data. Networks of spouts and bolts are packaged into a no ''topology'', which is submitted to storm cluster. A tweet has many features, such as text, short_url, latitude or longitude, retweet_count, etc. All these features can be useful for finding out useful information. To extract all theses features from tweets in real-time. This process is also known as a pre-processing analytic pipeline, because the extracted features and data help to pattern extraction module.
- Spout:
A spout use the Streaming API to crawl real-time tweets.
- Bolt:
The bolts contain computation logics to perform feature extraction logic in real-time. The first bolt is a filter bolt to identify the language of a tweet and allow only English tweets. Once all computing bolts are finished, the final bolt will save the data into the database.