Difference between revisions of "PC"
(→3.1 Semantic Computing (SC)) |
|||
| (16 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
[http://knoesis.org/amit Amit Sheth], [http://knoesis.org/researchers/pramod/ Pramod Anantharam], and [http://knoesis.org/researchers/cory/ Cory Henson]<br /><br /> | [http://knoesis.org/amit Amit Sheth], [http://knoesis.org/researchers/pramod/ Pramod Anantharam], and [http://knoesis.org/researchers/cory/ Cory Henson]<br /><br /> | ||
| − | + | While the debate about whether AI, robots, or machines will replace humans is raging (among Gates, Hawking, Musk, Theil and others), there remains a long tradition of viewpoints that take a progressively more human-centric view of computing. A range of viewpoints, from machine-centric to human-centric, have been put forward by McCarthy (intelligent machines), Weiser (Ubiquitous computing), Englebert (augmenting human intellect), Lickleider (man-machine symbiosis) and others. We focus on the recent progress taking place in human-centric visions, such as Computing for Human Experience (CHE) (Sheth) and Experiential Computing (Jain) [S10]. CHE is focused on serving people’s needs, empowering us while keeping us in loop, making us more productive with better and timely decision making, and improving and enriching our quality of life.<br/> | |
| + | The Web continues to evolve and serve as the infrastructure and intermediary that carries massive amounts of multimodal and multisensory observations, and facilitates reporting and sharing of observations. These observations capture various situations pertinent to people’s needs and interests along with all their idiosyncrasies. Data of relevance to people’s lives span the physical (reality, as measured by sensors/devices/IoT), cyber (all shared data and knowledge on the Web), and social (all the human interactions and conversations) spheres [SAH13]. Web data may contain event of interest to everyone (e.g., climate), to many (e.g., traffic), or to only one (something very personal such as asthma). These observations contribute toward shaping the human experience.<br/> | ||
| + | We emphasize contextual and personalized interpretation in processing such varying forms of data to make it more readily consumable and actionable for people. Toward this goal, we discuss the computing paradigms of semantic computing, cognitive computing, and an emerging paradigm in this lineage, which we term perceptual computing. In our view, these technologies offer a continuum to make the most out of vast, growing, and diverse data about many things that matter to people’s needs, interests, and experiences. This is achieved through actionable information, both when humans desire something (explicit) and through ambient understanding (implicit) of when something may be useful to people’s activities and decision making. Perceptual computing is characterized by its use of interpretation and exploration to actively interact with the surrounding environment in order to collect data of relevance useful for understanding the world around us.<br/> | ||
| + | This article consists of two parts. First we describe semantic computing, cognitive computing, and perceptual computing to lay out distinctions while acknowledging their complementary capabilities to support CHE. We then provide a conceptual overview of the newest of these three paradigms—perceptual computing. For further insights, we describe a scenario of asthma management and explain the computational contributions of semantic computing, cognitive computing, and perceptual computing in synthesizing actionable information. This is done through computational support for contextual and personalized processing of data into abstractions that raise it to the level of the human thought process and decision-making. | ||
| + | ==1. Challenge: Making the Web More Intelligent to Serve Humans Better== | ||
| + | As we continue to progress in developing technologies that disappear into the background, as envisaged by Mark Weiser [MW91], the next important focus of human-centered computing is to endow the Web, and computing in general, with sophisticated human-like capabilities to reduce information overload. In the near future, such capabilities will enable computing at a much larger scale than the human brain is able to handle, while still doing so in a highly contextual and personalized manner. This technology will provide more intimate support of our every decision and action, ultimately shaping the human experience. The three capabilities we consider include: semantics, cognition, and perception. While dictionary definitions for cognition and perception often have significant overlap, we will make a distinction based on how cognitive computing has been defined so far and on the complementary capabilities of perceptual computing. Over the next decade the development of these three computing paradigms—both individually and in cooperation—and their integration into the fabric of the Web will enable the emergence of a far more intelligent and human-centered Web. | ||
| + | ==2. Semantics, Cognition, and Perception== | ||
| + | Semantics, cognition, and perception have been used in a variety of situations. We would like to clarify our interpretation of these terms and also specify the connections between them in the context of human cognition and perception and how data (observations) relates to semantics, cognition, and perception. Accordingly, we ignore their use in other contexts; for example, the use of semantics in the context of programming languages, or perception in the context of people interacting with computing peripherals. | ||
| − | + | <b>Semantics</b> are the meanings attributed to concepts and their relations within the mind. This Web of concepts and relations are used to represent knowledge about the world. Such knowledge may then be utilized for interpreting our daily experiences through cognition and perception. Semantic concepts may represent (or unify, or subsume, or map to) various patterns of data, e.g., we may recognize a person by her face (visual signal) or by her voice (speech signal) but once recognized, both visual and speech signals represents a single semantic concept to a person. Semantics hide syntactic and representational differences in data and helps refer to data using a conceptual abstraction. Generally, this involves mapping observations from various physical stimuli such as visual or speech signals to concepts and relationships as humans would interpret and communicate. | |
| + | <b>Cognition</b> is an act of interpreting data in order to derive an understanding of the world around us. This interpretation is done by utilizing domain/background knowledge and reasoning. Interpretation involves pattern recognition and classification of patterns from sensory inputs generated from physical stimuli. Our interpretation of sensory inputs is robust to noise and impreciseness inherent in the environment. Interpretation converts multimodal and multi-sensory data from our senses to knowledge. Further, the derived knowledge can be utilized to gain insights or to answer questions. | ||
| + | <b>Perception</b> is also an act of interpreting data from the world around us. Unlike cognition on its own, perception utilizes sensing and actuation to actively explore the surrounding environment in order to collect data of relevance. This data may then be used by our cognitive facilities to more effectively understand the world around us. Perception involves interpretation and exploration, with a strong reliance on background knowledge [G97]. | ||
| + | Perception is a cyclical process of interpretation and exploration of data utilizing associated cognition. Perception constantly attempts to match incoming sensory inputs (and engage associated cognition) with top-down expectations or predictions (based on cognition), and closely integrates with human actions. While the outcome of cognition results in understanding of our environment, the act of perception results in applying our understanding for asking the right (contextually relevant) question. | ||
| − | + | <b>Exploring Connections</b> | |
| − | + | Perception and cognition utilize semantics for associating meaning with observations, resulting in the integration of heterogeneous observations. Both perception and cognition deal with the interpretation of observations. However, perception further explores the observation space, which is influenced by the current knowledge of the domain and the environmental observations (cognition). Perception acts as a bootstrapping process between observations and the knowledge of the domain resulting in the improvement of the domain knowledge. | |
| − | + | ==3. Computational Aspects of Semantics, Cognition, and Perception== | |
| + | For conceptual clarity and general understanding of what the three terms mean, we exemplify semantics, cognition, and perception using a real-world scenario of asthma management. Asthma is a multifaceted, highly contextual, and personal disease. Multifaceted since asthma is characterized by many aspects such as triggers in environment and patient sensitiveness to triggers. Contextual since events of interest, such as the location of the person and triggers at a location, are crucial for timely alerts. Personal since asthma patients have varying responses to triggers and their actions vary based on the severity of their condition. | ||
| − | + | Asthma patients are characterized by two measures as used by clinical guidelines: severity level and control level. The severity level is diagnosed by a doctor and can take one of four states: mild, mild persistent, moderate, and severe. The control level indicates the extent of asthma exacerbations and can take one of three states: well controlled, moderately controlled, and poorly controlled. Patients don’t change their severity level often, but their control level may vary drastically depending on triggers, environmental conditions, medication, and symptomatic variations of the patient. | |
| − | + | Let’s consider an asthma patient, Anna who is age 10 and has been diagnosed with ‘severe’ asthma. She is quite disciplined with her medication and avoids exposure to triggers, resulting in a control level of ‘well controlled’. She receives an invitation from her friend to play soccer in a few days. Now, she and her parents must maintain a balance between her longing to play in the soccer match and the need to avoid exacerbating her asthma. | |
| − | For example, | + | The solution to this dilemma is not straightforward and cannot be answered using only existing factual information found on the Web, in medical books or journals, or electronic medical records. Knowledge found on the Web may contain common knowledge about asthma, but it may not be directly applicable to Anna. For example, while there may be websites [ATM14] describing general symptoms, triggers, and tips for better asthma management, Anna and her parents may not be able to use this information since her symptomatic variations for environmental triggers may be unique. While medical domain knowledge of asthma in the form of publications (e.g., PubMed) may contain symptomatic variations for various triggers, it is challenging to apply this knowledge to Anna’s specific case even though it may be described in her electronic medical records. Furthermore, such an application of knowledge would not consider any environmental and physiological dynamics of Anna or her quality of life choices. |
| + | <br/>We will explore the semantic, cognitive, and perceptual computing and then explain their role in providing a solution to the asthma problem. | ||
| + | ===3.1 Semantic Computing (SC)=== | ||
| + | SC encompasses technology for representing concepts and their relations in an integrated semantic network that loosely mimics the inter-relation of concepts in the human mind. This conceptual knowledge, represented formally in the form of an ontology, can be used to annotate data and infer new knowledge from interpreted data (e.g., to infer expectations of cognized concepts). Additionally, SC plays a crucial role in dealing with multisensory and multimodal observations, leading to the integration of observations from diverse sources (see “horizontal operators” in [SAH13]). SC has a rich history of over 15 years [S14] resulting in various annotation standards for a variety of data (e.g., social and sensor data [C12] are in use). The annotated data is used for interpretation by cognitive and perceptual computing. Figure 1 has SC as a vertical box through which the interpretation and exploration are routed (further explained in Section 3.3). SC also provides languages for formal representation of background knowledge. | ||
| − | + | The semantic network of general medical domain knowledge related to asthma and its symptoms define asthma control levels in terms of symptoms. This general knowledge may be integrated with knowledge of Anna’s specific case found in her EMR. The weather, pollen, and air quality index information observed by sensors may be available through web services. These annotated observations spanning multiple modalities, general domain knowledge, and context-specific knowledge (Anna’s asthma severity and control level) pose a great challenge for its interpretation. The interpretation of observations needs background knowledge and, unfortunately, Anna’s parents do not posses such asthma-related knowledge. Anna and her parents are left with no particular insights at this step since manually interpreting all the observations is not a practical solution. In the next two subsections, we describe the interpretation of data using domain knowledge for deriving deeper insights. | |
| − | + | [[File:PC.png|Figure 1. Conceptual distinctions between perceptual, cognitive, and semantic computing along with the demonstration of the cyclical process of perceptual computing]]<br/>Figure 1. Conceptual distinctions between perceptual, cognitive, and semantic computing along with the demonstration of the cyclical process of perceptual computing | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ===3.2 Cognitive Computing (CC)=== | |
| + | DARPA, when launching a project on cognitive computing in 2002 had defined it as “reason[ing], [the] use [of] represented knowledge, learn[ing] from experience, accumulat[ing] knowledge, explain[ing] itself, accept[ing] direction, be[ing] aware of its own behavior and capabilities as well as respond[ing] in a robust manner to surprises.” Cognitive hardware architectures and cognitive algorithms are two broad focus areas of current research in CC. Cognitive algorithms interpret data by learning and matching patterns in a way that loosely mimics the process of cognition in the human mind. Cognitive systems learn from their experiences and then get better when performing repeated tasks. CC acts as prosthetics for human cognition by analyzing a massive amount of data and being able to answer questions humans may have when making certain decisions. One such example is IBM Watson which won the game show Jeopardy! in early 2011. The IBM Watson approach (albeit, not the technology) is now extended to medicine to aid doctors in clinical decisions. CC interprets annotated observations obtained from SC or raw observations from diverse sources and presents the result of the interpretation to humans. Humans, in turn, utilize the interpretation to perform action, which go on to form additional input for the CC system. CC systems utilize machine learning and other AI techniques in achieving all this without being explicitly programmed. Figure 1 shows the interpretation of observations by CC utilizing background knowledge. | ||
| − | + | Bewildered by the challenges in making the decision, Anna’s parents contact Anna’s pediatrician, Dr. Jones, for help. Let’s assume that Dr. Jones has access to a CC system such as IBM Watson for medicine and specifically for asthma management [W15]. Consequently, Dr. Jones is assisted by a CC system that can analyze massive amounts of medical literature, electronic medical records (EMRs), and clinical outcomes for asthma patients. Such a system would be instrumental in extending the cognitive abilities of Dr. Jones (minimizing the cognitive overload caused by the ever increasing research literature). Dr. Jones discovers from medical literature and EMRs that people with well-controlled asthma (i.e., patients who match with Anna) can indeed engage in physical activities if under the influence of appropriate preventive medication. Dr. Jones is still unclear about the vulnerability of Anna’s asthma control level due to weather and air quality index fluctuations. Dr. Jones lacks personalized and contextualized knowledge about Anna’s day-to-day environment, rendering him ill-informed in making any recommendation to Anna. | |
| − | + | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | === | + | ===3.3 Perceptual Computing (PC)=== |
| − | + | Socrates taught that knowledge is attained through the careful and deliberate process of asking and answering questions. Through data mining, pattern recognition, and natural language processing, CC has provided a technology to support our ability to answer complex questions. PC will complete the loop by providing a technology to support our ability to ask contextually relevant and personalized questions. PC complements SC and CC by providing machinery to ask the next question, aiding decision makers in gaining actionable insights. In other words, determining what data is most relevant in helping to disambiguate between the multiple possible causes (of Anna’s asthma condition, for example). If the expectations derived by utilizing domain knowledge and observations from the real world do not match the real-world outcomes, PC updates the knowledge of the real world. Through focused attention, utilizing sensing and actuation technologies, this relevant data is sought in the Physical-Cyber-Social environments. PC envisions the more effective interpretation of data through a cyclical process of interpretation and exploration in a way that loosely mimics the process of perception in the human mind and body. Neisser defines perception as “an active, cyclical process of exploration and interpretation [N67]." Machine perception is the process of converting sensor observations to abstractions through a cyclical process of interpretation and exploration utilizing background knowledge [HST12]. While CC efforts to date have investigated the interpretation of data, it has yet to adequately address the relationship between the interpretation of data and the exploration of (or interaction with) the environment. Additionally, PC involves the highly personalized and contextualized refinement of background knowledge by engaging in the cyclical process of interpretation and exploration. Interpretation is analogous to bottom-brain operation of processing observations from our senses and exploration compares to the top-brain processing of making/adapting plans to solve problems [K13]. This type of interaction—often involving focused attention and physical actuation—enables the perceiver to collect and retain data of relevance (from the ocean of all possible data), and thus it facilitates a more efficient, personalized interpretation or abstraction. Figure 1 demonstrates the cyclical process of PC involving interpretation and exploration. The interpretation of observations leads to abstractions (a concept in the background knowledge) and exploration leads to actuation for constraining the search space of relevant observations. | |
| − | + | A PC system may be implemented as an intelligence at the edge technology [HTS12], as opposed to a logically-centralized system that processes the massive amounts of data on the Web. In the case of Anna, a CC system processed all the medical knowledge, EMRs, and patient outcomes to provide information to Dr. Jones who then applied it to Anna’s case (personalization). Dr. Jones faced challenges in interpreting weather and air quality index with respect to vulnerability of Anna’s asthma control level. With the PC system being at the edge (closer to Anna, possibly realized as a mobile application with inputs from multiple sensors, such as kHealth: http://wiki.knoesis.org/index.php/Asthma), it actively engages in the cyclical process of interpretation and exploration. For example, Anna in the last month exhibited reduced activity during a soccer practice. This observation is interpreted by a PC system as an instance of asthma exacerbation. Further, a PC system actively seeks observations (asking questions by a PC system) for weather and the air quality index to determine their effect on the asthma symptoms of Anna. A PC system will be able to take generic background knowledge (poor air quality may cause asthma exacerbations) for exploration and add contextual and personalized knowledge (poor air quality exposure of Anna may cause asthma exacerbations to Anna). Dr. Jones can be presented with these pieces of information along with the information from the CC component. Anna is advised to refrain from the soccer match due to poor air quality on the day of the soccer game. This information will be valuable to Anna and her parents, possibly resulting in Anna avoiding conditions and/or situations, which may lead to the exacerbation of her asthma. | |
| − | == | + | ==4.Conclusions== |
| − | + | Perceptual computing is an evolution of cognitive computing, in which computers can not only provide answers to the complex questions posed to them but can also subsequently ask the right follow up questions and then interact with the environment—either physical, cyber, or social—to collect the relevant data. As PC evolves, the personalization components would extend to include temporal and spatial context, and others factors that drive human decisions and actions, such as emotions, and cultural and social preferences. This will enable more effective answers, better decisions and timely actions that are specifically tailored to each person. We envision the cyclical process of PC to evolve background knowledge toward contextualization and personalization. We demonstrated PC and its complementary nature to SC and CC by taking a concrete, real-world example of asthma management. The Internet of Things, often hailed as the next great phase of the Web, with its emphasis on sensing and actuation will exploit all these three forms of computing. | |
| − | + | ==References== | |
| + | [ATM15] Asthma Triggers and Management: Tips to Remember, http://www.aaaai.org/conditions-and-treatments/library/asthma-library/asthma-triggers-and-management.aspx (Accessed Jan 18, 2015) <br/> | ||
| + | [C12] Michael Compton, et al. "The SSN ontology of the W3C semantic sensor network incubator group." Web Semantics: Science, Services and Agents on the World Wide Web 17 (2012): 25-32. <br/> | ||
| − | + | [C13] Andy Clark. "Whatever next? Predictive brains, situated agents, and the future of cognitive science." Behavioral and Brain Sciences 36.03 (2013): 181-204. <br/> | |
| − | [ | + | [G97] Richard Gregory. "Knowledge in perception and illusion," Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London, Series B: Biological Sciences 352.1358 (1997): 1121-1127. <br/> |
| − | + | [HST12] Cory Henson, Amit Sheth, Krishnaprasad Thirunarayan. 'Semantic Perception: Converting Sensory Observations to Abstractions,' IEEE Internet Computing, vol. 16, no. 2, pp. 26-34, Mar./Apr. 2012 <br/> | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | [HTS12] Cory Henson, Krishnaprasad Thirunarayan, and Amit Sheth. 'An Efficient Bit Vector Approach to Semantics-based Machine Perception in Resource-Constrained Devices,' 11th International Semantic Web Conference (ISWC 2012), Boston, Massachusetts, USA, November 11-15, 2012. <br/> | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | [ | + | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | [ | + | [MW91] Mark Weiser. “The Computer for the 21st Century,” Scientific American, 265 (3), September 1991, pp. 94-104. <br/> |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | [N67] Ulric Neisser. "Cognitive psychology." (1967). <br/> | |
| − | + | ||
| + | [S10] Amit Sheth. 'Computing for Human Experience: Semantics-Empowered Sensors, Services, and Social Computing on the Ubiquitous Web,' IEEE Internet Computing 14(1), pp. 88-91, Jan./Feb. 2010 <br/> | ||
| + | [SAH13] Ami Sheth, Pramod Anantharam, Cory Henson. 'Physical-Cyber-Social Computing: An Early 21st Century Approach,' IEEE Intelligent Systems, pp. 79-82, Jan./Feb. 2013 <br/> | ||
| − | + | [S14] Amit Sheth 15 years of Semantic Search and Ontology-enabled Semantic Applications, Amit Sheth, http://amitsheth.blogspot.com/2014/09/15-years-of-semantic-search-and.html (Accessed Jan 21, 2015) <br/> | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | [W15] IBMs Watson may soon be the best doctor in the world, | |
| − | + | http://www.businessinsider.com/ibms-watson-may-soon-be-the-best-doctor-in-the-world-2014-4 (Accessed Jan 20, 2015) <br/> | |
| − | + | [K13] Stephen Michael, and Stephen Kosslyn. Top Brain, Bottom Brain: Surprising Insights Into how You Think. Simon and Schuster, 2013. <br/> | |
Latest revision as of 20:33, 21 May 2015
Semantic, Cognitive and Perceptual Computing:
Advances toward Computing for Human Experience
Amit Sheth, Pramod Anantharam, and Cory Henson
While the debate about whether AI, robots, or machines will replace humans is raging (among Gates, Hawking, Musk, Theil and others), there remains a long tradition of viewpoints that take a progressively more human-centric view of computing. A range of viewpoints, from machine-centric to human-centric, have been put forward by McCarthy (intelligent machines), Weiser (Ubiquitous computing), Englebert (augmenting human intellect), Lickleider (man-machine symbiosis) and others. We focus on the recent progress taking place in human-centric visions, such as Computing for Human Experience (CHE) (Sheth) and Experiential Computing (Jain) [S10]. CHE is focused on serving people’s needs, empowering us while keeping us in loop, making us more productive with better and timely decision making, and improving and enriching our quality of life.
The Web continues to evolve and serve as the infrastructure and intermediary that carries massive amounts of multimodal and multisensory observations, and facilitates reporting and sharing of observations. These observations capture various situations pertinent to people’s needs and interests along with all their idiosyncrasies. Data of relevance to people’s lives span the physical (reality, as measured by sensors/devices/IoT), cyber (all shared data and knowledge on the Web), and social (all the human interactions and conversations) spheres [SAH13]. Web data may contain event of interest to everyone (e.g., climate), to many (e.g., traffic), or to only one (something very personal such as asthma). These observations contribute toward shaping the human experience.
We emphasize contextual and personalized interpretation in processing such varying forms of data to make it more readily consumable and actionable for people. Toward this goal, we discuss the computing paradigms of semantic computing, cognitive computing, and an emerging paradigm in this lineage, which we term perceptual computing. In our view, these technologies offer a continuum to make the most out of vast, growing, and diverse data about many things that matter to people’s needs, interests, and experiences. This is achieved through actionable information, both when humans desire something (explicit) and through ambient understanding (implicit) of when something may be useful to people’s activities and decision making. Perceptual computing is characterized by its use of interpretation and exploration to actively interact with the surrounding environment in order to collect data of relevance useful for understanding the world around us.
This article consists of two parts. First we describe semantic computing, cognitive computing, and perceptual computing to lay out distinctions while acknowledging their complementary capabilities to support CHE. We then provide a conceptual overview of the newest of these three paradigms—perceptual computing. For further insights, we describe a scenario of asthma management and explain the computational contributions of semantic computing, cognitive computing, and perceptual computing in synthesizing actionable information. This is done through computational support for contextual and personalized processing of data into abstractions that raise it to the level of the human thought process and decision-making.
Contents
1. Challenge: Making the Web More Intelligent to Serve Humans Better
As we continue to progress in developing technologies that disappear into the background, as envisaged by Mark Weiser [MW91], the next important focus of human-centered computing is to endow the Web, and computing in general, with sophisticated human-like capabilities to reduce information overload. In the near future, such capabilities will enable computing at a much larger scale than the human brain is able to handle, while still doing so in a highly contextual and personalized manner. This technology will provide more intimate support of our every decision and action, ultimately shaping the human experience. The three capabilities we consider include: semantics, cognition, and perception. While dictionary definitions for cognition and perception often have significant overlap, we will make a distinction based on how cognitive computing has been defined so far and on the complementary capabilities of perceptual computing. Over the next decade the development of these three computing paradigms—both individually and in cooperation—and their integration into the fabric of the Web will enable the emergence of a far more intelligent and human-centered Web.
2. Semantics, Cognition, and Perception
Semantics, cognition, and perception have been used in a variety of situations. We would like to clarify our interpretation of these terms and also specify the connections between them in the context of human cognition and perception and how data (observations) relates to semantics, cognition, and perception. Accordingly, we ignore their use in other contexts; for example, the use of semantics in the context of programming languages, or perception in the context of people interacting with computing peripherals.
Semantics are the meanings attributed to concepts and their relations within the mind. This Web of concepts and relations are used to represent knowledge about the world. Such knowledge may then be utilized for interpreting our daily experiences through cognition and perception. Semantic concepts may represent (or unify, or subsume, or map to) various patterns of data, e.g., we may recognize a person by her face (visual signal) or by her voice (speech signal) but once recognized, both visual and speech signals represents a single semantic concept to a person. Semantics hide syntactic and representational differences in data and helps refer to data using a conceptual abstraction. Generally, this involves mapping observations from various physical stimuli such as visual or speech signals to concepts and relationships as humans would interpret and communicate.
Cognition is an act of interpreting data in order to derive an understanding of the world around us. This interpretation is done by utilizing domain/background knowledge and reasoning. Interpretation involves pattern recognition and classification of patterns from sensory inputs generated from physical stimuli. Our interpretation of sensory inputs is robust to noise and impreciseness inherent in the environment. Interpretation converts multimodal and multi-sensory data from our senses to knowledge. Further, the derived knowledge can be utilized to gain insights or to answer questions.
Perception is also an act of interpreting data from the world around us. Unlike cognition on its own, perception utilizes sensing and actuation to actively explore the surrounding environment in order to collect data of relevance. This data may then be used by our cognitive facilities to more effectively understand the world around us. Perception involves interpretation and exploration, with a strong reliance on background knowledge [G97].
Perception is a cyclical process of interpretation and exploration of data utilizing associated cognition. Perception constantly attempts to match incoming sensory inputs (and engage associated cognition) with top-down expectations or predictions (based on cognition), and closely integrates with human actions. While the outcome of cognition results in understanding of our environment, the act of perception results in applying our understanding for asking the right (contextually relevant) question.
Exploring Connections Perception and cognition utilize semantics for associating meaning with observations, resulting in the integration of heterogeneous observations. Both perception and cognition deal with the interpretation of observations. However, perception further explores the observation space, which is influenced by the current knowledge of the domain and the environmental observations (cognition). Perception acts as a bootstrapping process between observations and the knowledge of the domain resulting in the improvement of the domain knowledge.
3. Computational Aspects of Semantics, Cognition, and Perception
For conceptual clarity and general understanding of what the three terms mean, we exemplify semantics, cognition, and perception using a real-world scenario of asthma management. Asthma is a multifaceted, highly contextual, and personal disease. Multifaceted since asthma is characterized by many aspects such as triggers in environment and patient sensitiveness to triggers. Contextual since events of interest, such as the location of the person and triggers at a location, are crucial for timely alerts. Personal since asthma patients have varying responses to triggers and their actions vary based on the severity of their condition.
Asthma patients are characterized by two measures as used by clinical guidelines: severity level and control level. The severity level is diagnosed by a doctor and can take one of four states: mild, mild persistent, moderate, and severe. The control level indicates the extent of asthma exacerbations and can take one of three states: well controlled, moderately controlled, and poorly controlled. Patients don’t change their severity level often, but their control level may vary drastically depending on triggers, environmental conditions, medication, and symptomatic variations of the patient.
Let’s consider an asthma patient, Anna who is age 10 and has been diagnosed with ‘severe’ asthma. She is quite disciplined with her medication and avoids exposure to triggers, resulting in a control level of ‘well controlled’. She receives an invitation from her friend to play soccer in a few days. Now, she and her parents must maintain a balance between her longing to play in the soccer match and the need to avoid exacerbating her asthma.
The solution to this dilemma is not straightforward and cannot be answered using only existing factual information found on the Web, in medical books or journals, or electronic medical records. Knowledge found on the Web may contain common knowledge about asthma, but it may not be directly applicable to Anna. For example, while there may be websites [ATM14] describing general symptoms, triggers, and tips for better asthma management, Anna and her parents may not be able to use this information since her symptomatic variations for environmental triggers may be unique. While medical domain knowledge of asthma in the form of publications (e.g., PubMed) may contain symptomatic variations for various triggers, it is challenging to apply this knowledge to Anna’s specific case even though it may be described in her electronic medical records. Furthermore, such an application of knowledge would not consider any environmental and physiological dynamics of Anna or her quality of life choices.
We will explore the semantic, cognitive, and perceptual computing and then explain their role in providing a solution to the asthma problem.
3.1 Semantic Computing (SC)
SC encompasses technology for representing concepts and their relations in an integrated semantic network that loosely mimics the inter-relation of concepts in the human mind. This conceptual knowledge, represented formally in the form of an ontology, can be used to annotate data and infer new knowledge from interpreted data (e.g., to infer expectations of cognized concepts). Additionally, SC plays a crucial role in dealing with multisensory and multimodal observations, leading to the integration of observations from diverse sources (see “horizontal operators” in [SAH13]). SC has a rich history of over 15 years [S14] resulting in various annotation standards for a variety of data (e.g., social and sensor data [C12] are in use). The annotated data is used for interpretation by cognitive and perceptual computing. Figure 1 has SC as a vertical box through which the interpretation and exploration are routed (further explained in Section 3.3). SC also provides languages for formal representation of background knowledge.
The semantic network of general medical domain knowledge related to asthma and its symptoms define asthma control levels in terms of symptoms. This general knowledge may be integrated with knowledge of Anna’s specific case found in her EMR. The weather, pollen, and air quality index information observed by sensors may be available through web services. These annotated observations spanning multiple modalities, general domain knowledge, and context-specific knowledge (Anna’s asthma severity and control level) pose a great challenge for its interpretation. The interpretation of observations needs background knowledge and, unfortunately, Anna’s parents do not posses such asthma-related knowledge. Anna and her parents are left with no particular insights at this step since manually interpreting all the observations is not a practical solution. In the next two subsections, we describe the interpretation of data using domain knowledge for deriving deeper insights.
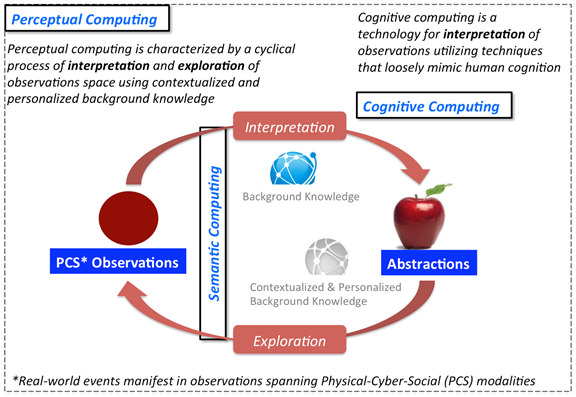
Figure 1. Conceptual distinctions between perceptual, cognitive, and semantic computing along with the demonstration of the cyclical process of perceptual computing
3.2 Cognitive Computing (CC)
DARPA, when launching a project on cognitive computing in 2002 had defined it as “reason[ing], [the] use [of] represented knowledge, learn[ing] from experience, accumulat[ing] knowledge, explain[ing] itself, accept[ing] direction, be[ing] aware of its own behavior and capabilities as well as respond[ing] in a robust manner to surprises.” Cognitive hardware architectures and cognitive algorithms are two broad focus areas of current research in CC. Cognitive algorithms interpret data by learning and matching patterns in a way that loosely mimics the process of cognition in the human mind. Cognitive systems learn from their experiences and then get better when performing repeated tasks. CC acts as prosthetics for human cognition by analyzing a massive amount of data and being able to answer questions humans may have when making certain decisions. One such example is IBM Watson which won the game show Jeopardy! in early 2011. The IBM Watson approach (albeit, not the technology) is now extended to medicine to aid doctors in clinical decisions. CC interprets annotated observations obtained from SC or raw observations from diverse sources and presents the result of the interpretation to humans. Humans, in turn, utilize the interpretation to perform action, which go on to form additional input for the CC system. CC systems utilize machine learning and other AI techniques in achieving all this without being explicitly programmed. Figure 1 shows the interpretation of observations by CC utilizing background knowledge.
Bewildered by the challenges in making the decision, Anna’s parents contact Anna’s pediatrician, Dr. Jones, for help. Let’s assume that Dr. Jones has access to a CC system such as IBM Watson for medicine and specifically for asthma management [W15]. Consequently, Dr. Jones is assisted by a CC system that can analyze massive amounts of medical literature, electronic medical records (EMRs), and clinical outcomes for asthma patients. Such a system would be instrumental in extending the cognitive abilities of Dr. Jones (minimizing the cognitive overload caused by the ever increasing research literature). Dr. Jones discovers from medical literature and EMRs that people with well-controlled asthma (i.e., patients who match with Anna) can indeed engage in physical activities if under the influence of appropriate preventive medication. Dr. Jones is still unclear about the vulnerability of Anna’s asthma control level due to weather and air quality index fluctuations. Dr. Jones lacks personalized and contextualized knowledge about Anna’s day-to-day environment, rendering him ill-informed in making any recommendation to Anna.
3.3 Perceptual Computing (PC)
Socrates taught that knowledge is attained through the careful and deliberate process of asking and answering questions. Through data mining, pattern recognition, and natural language processing, CC has provided a technology to support our ability to answer complex questions. PC will complete the loop by providing a technology to support our ability to ask contextually relevant and personalized questions. PC complements SC and CC by providing machinery to ask the next question, aiding decision makers in gaining actionable insights. In other words, determining what data is most relevant in helping to disambiguate between the multiple possible causes (of Anna’s asthma condition, for example). If the expectations derived by utilizing domain knowledge and observations from the real world do not match the real-world outcomes, PC updates the knowledge of the real world. Through focused attention, utilizing sensing and actuation technologies, this relevant data is sought in the Physical-Cyber-Social environments. PC envisions the more effective interpretation of data through a cyclical process of interpretation and exploration in a way that loosely mimics the process of perception in the human mind and body. Neisser defines perception as “an active, cyclical process of exploration and interpretation [N67]." Machine perception is the process of converting sensor observations to abstractions through a cyclical process of interpretation and exploration utilizing background knowledge [HST12]. While CC efforts to date have investigated the interpretation of data, it has yet to adequately address the relationship between the interpretation of data and the exploration of (or interaction with) the environment. Additionally, PC involves the highly personalized and contextualized refinement of background knowledge by engaging in the cyclical process of interpretation and exploration. Interpretation is analogous to bottom-brain operation of processing observations from our senses and exploration compares to the top-brain processing of making/adapting plans to solve problems [K13]. This type of interaction—often involving focused attention and physical actuation—enables the perceiver to collect and retain data of relevance (from the ocean of all possible data), and thus it facilitates a more efficient, personalized interpretation or abstraction. Figure 1 demonstrates the cyclical process of PC involving interpretation and exploration. The interpretation of observations leads to abstractions (a concept in the background knowledge) and exploration leads to actuation for constraining the search space of relevant observations.
A PC system may be implemented as an intelligence at the edge technology [HTS12], as opposed to a logically-centralized system that processes the massive amounts of data on the Web. In the case of Anna, a CC system processed all the medical knowledge, EMRs, and patient outcomes to provide information to Dr. Jones who then applied it to Anna’s case (personalization). Dr. Jones faced challenges in interpreting weather and air quality index with respect to vulnerability of Anna’s asthma control level. With the PC system being at the edge (closer to Anna, possibly realized as a mobile application with inputs from multiple sensors, such as kHealth: http://wiki.knoesis.org/index.php/Asthma), it actively engages in the cyclical process of interpretation and exploration. For example, Anna in the last month exhibited reduced activity during a soccer practice. This observation is interpreted by a PC system as an instance of asthma exacerbation. Further, a PC system actively seeks observations (asking questions by a PC system) for weather and the air quality index to determine their effect on the asthma symptoms of Anna. A PC system will be able to take generic background knowledge (poor air quality may cause asthma exacerbations) for exploration and add contextual and personalized knowledge (poor air quality exposure of Anna may cause asthma exacerbations to Anna). Dr. Jones can be presented with these pieces of information along with the information from the CC component. Anna is advised to refrain from the soccer match due to poor air quality on the day of the soccer game. This information will be valuable to Anna and her parents, possibly resulting in Anna avoiding conditions and/or situations, which may lead to the exacerbation of her asthma.
4.Conclusions
Perceptual computing is an evolution of cognitive computing, in which computers can not only provide answers to the complex questions posed to them but can also subsequently ask the right follow up questions and then interact with the environment—either physical, cyber, or social—to collect the relevant data. As PC evolves, the personalization components would extend to include temporal and spatial context, and others factors that drive human decisions and actions, such as emotions, and cultural and social preferences. This will enable more effective answers, better decisions and timely actions that are specifically tailored to each person. We envision the cyclical process of PC to evolve background knowledge toward contextualization and personalization. We demonstrated PC and its complementary nature to SC and CC by taking a concrete, real-world example of asthma management. The Internet of Things, often hailed as the next great phase of the Web, with its emphasis on sensing and actuation will exploit all these three forms of computing.
References
[ATM15] Asthma Triggers and Management: Tips to Remember, http://www.aaaai.org/conditions-and-treatments/library/asthma-library/asthma-triggers-and-management.aspx (Accessed Jan 18, 2015)
[C12] Michael Compton, et al. "The SSN ontology of the W3C semantic sensor network incubator group." Web Semantics: Science, Services and Agents on the World Wide Web 17 (2012): 25-32.
[C13] Andy Clark. "Whatever next? Predictive brains, situated agents, and the future of cognitive science." Behavioral and Brain Sciences 36.03 (2013): 181-204.
[G97] Richard Gregory. "Knowledge in perception and illusion," Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London, Series B: Biological Sciences 352.1358 (1997): 1121-1127.
[HST12] Cory Henson, Amit Sheth, Krishnaprasad Thirunarayan. 'Semantic Perception: Converting Sensory Observations to Abstractions,' IEEE Internet Computing, vol. 16, no. 2, pp. 26-34, Mar./Apr. 2012
[HTS12] Cory Henson, Krishnaprasad Thirunarayan, and Amit Sheth. 'An Efficient Bit Vector Approach to Semantics-based Machine Perception in Resource-Constrained Devices,' 11th International Semantic Web Conference (ISWC 2012), Boston, Massachusetts, USA, November 11-15, 2012.
[MW91] Mark Weiser. “The Computer for the 21st Century,” Scientific American, 265 (3), September 1991, pp. 94-104.
[N67] Ulric Neisser. "Cognitive psychology." (1967).
[S10] Amit Sheth. 'Computing for Human Experience: Semantics-Empowered Sensors, Services, and Social Computing on the Ubiquitous Web,' IEEE Internet Computing 14(1), pp. 88-91, Jan./Feb. 2010
[SAH13] Ami Sheth, Pramod Anantharam, Cory Henson. 'Physical-Cyber-Social Computing: An Early 21st Century Approach,' IEEE Intelligent Systems, pp. 79-82, Jan./Feb. 2013
[S14] Amit Sheth 15 years of Semantic Search and Ontology-enabled Semantic Applications, Amit Sheth, http://amitsheth.blogspot.com/2014/09/15-years-of-semantic-search-and.html (Accessed Jan 21, 2015)
[W15] IBMs Watson may soon be the best doctor in the world,
http://www.businessinsider.com/ibms-watson-may-soon-be-the-best-doctor-in-the-world-2014-4 (Accessed Jan 20, 2015)
[K13] Stephen Michael, and Stephen Kosslyn. Top Brain, Bottom Brain: Surprising Insights Into how You Think. Simon and Schuster, 2013.