Difference between revisions of "KHealthAsthmaOntology"
| Line 22: | Line 22: | ||
[http://knoesis.org/ontology/kHhealth/Asthma/schema.ttl kao ontology code V1] (designed in 2016 by SoonJye Kho and Utkarshani Jaimini) | [http://knoesis.org/ontology/kHhealth/Asthma/schema.ttl kao ontology code V1] (designed in 2016 by SoonJye Kho and Utkarshani Jaimini) | ||
| − | = Kao Ontology: Best Practices with PerfectO (ONGOING) = | + | |
| + | |||
| + | = kao Evaluation (ONGOING) = | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Kao Ontology used for automatic semantic annotation and reasoning (ONGOING) == | ||
| + | |||
| + | The kao ontology is used to semantically annotate the IoT datasaset using [https://jena.apache.org/ Jena, a framework to build semantic web applications]. | ||
| + | High-level abstractions (e.g., HighgPollenLevel) can be deduced by executing the [http://linkedopenreasoning.appspot.com/?p=slorv2 Sensor-based Linked Open Reasoning (S-LOR)] inference engine based on the Jena inference engine. | ||
| + | S-LOR inference engine is being extended for health measurements or any IoT dasets used within the kHealth project. | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Kao Ontology: Best Practices with PerfectO (ONGOING) == | ||
We follow as much as possible the [http://perfectsemanticweb.appspot.com/?p=ontologyValidation PerfectO methodology] to improve the quality of the ontology and its integration with useful ontology tools to provide automatic documentation visualization, etc. | We follow as much as possible the [http://perfectsemanticweb.appspot.com/?p=ontologyValidation PerfectO methodology] to improve the quality of the ontology and its integration with useful ontology tools to provide automatic documentation visualization, etc. | ||
| Line 42: | Line 52: | ||
[[File:KaoBestPractices4.png|700px|thumb|center|Kao Ontology: Best Practices with PerfectO]] | [[File:KaoBestPractices4.png|700px|thumb|center|Kao Ontology: Best Practices with PerfectO]] | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
= References = | = References = | ||
Revision as of 20:06, 10 July 2018
Contents
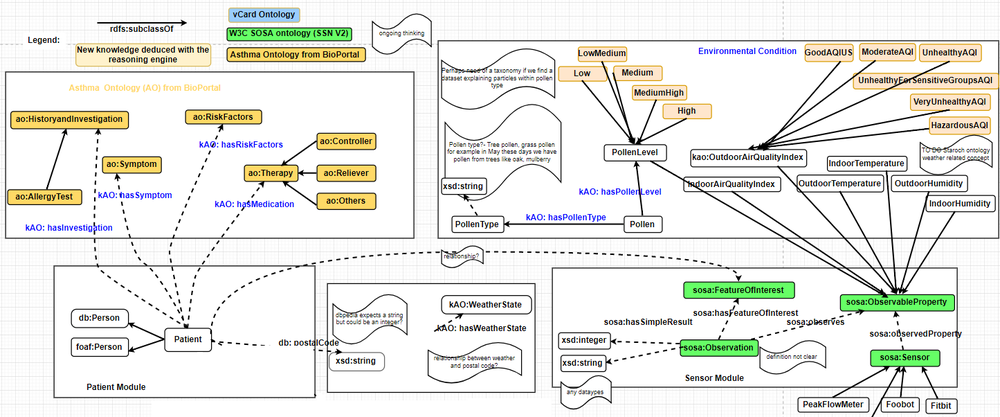
Knoesis Asthma Ontology (KAO)
The Knoesis Asthma Ontology (KAO) is being designed to deduce abstractions from the asthma dataset provided by the kHealth project.
The asthma dataset collects data generated by IoT devices such as peak flow meter, Foobot, Fitbit, AirNow, and other Web Services obtaining parameters such as air quality, pollen index, outside humidity and temperature.
kao Overview (ONGOING)
The knoesis Asthma Ontology (kAO) ontology is being created and reused ontologies as follows:
- W3C Semantic Sensor Network (SSN) and Sensor, Observation, Sample, and Actuator (SOSA) ontologies to semantically annotate sensor observations (e.g., peak flow meter is a subclass of the sosa:Sensor class)
- Asthma Ontology (AO ontology) from BioPortal to reuse relevant concepts
- FOAF ontology to describe people
- Weather ontology [Staroch 2013] [Kofler et al. 2011] to deduce meaningful information from weather datasets.
kao Ontology Implementation (ONGOING)
kao ontology code V2 (designed in 2018 by Utkarshani Jaimini and Amelie Gyrard)
kao ontology code V1 (designed in 2016 by SoonJye Kho and Utkarshani Jaimini)
kao Evaluation (ONGOING)
Kao Ontology used for automatic semantic annotation and reasoning (ONGOING)
The kao ontology is used to semantically annotate the IoT datasaset using Jena, a framework to build semantic web applications. High-level abstractions (e.g., HighgPollenLevel) can be deduced by executing the Sensor-based Linked Open Reasoning (S-LOR) inference engine based on the Jena inference engine. S-LOR inference engine is being extended for health measurements or any IoT dasets used within the kHealth project.
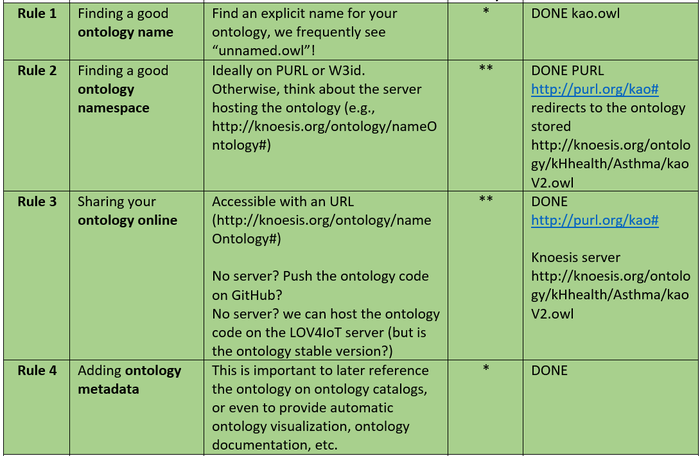
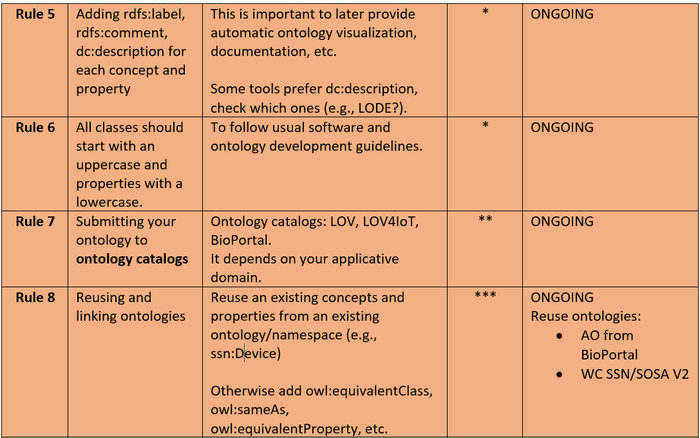
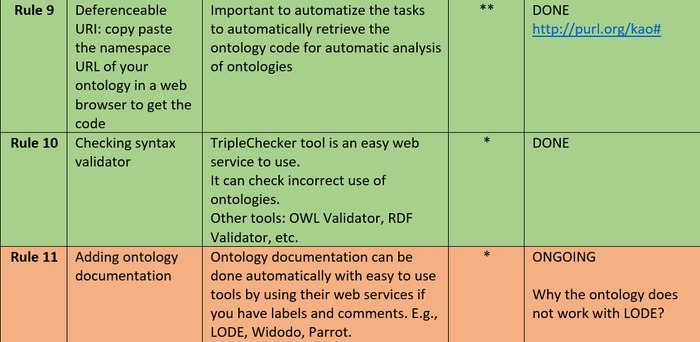
Kao Ontology: Best Practices with PerfectO (ONGOING)
We follow as much as possible the PerfectO methodology to improve the quality of the ontology and its integration with useful ontology tools to provide automatic documentation visualization, etc.
- PURL to get a permanent URL: http://purl.org/kao#
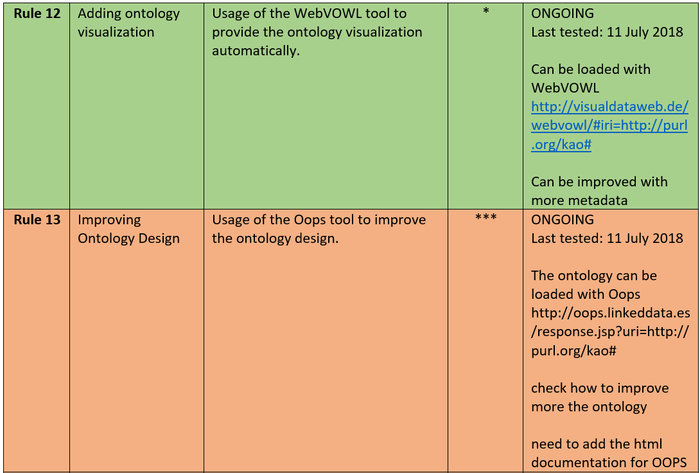
- Usage of the WebVOWL tool to provide the ontology visualization automatically: http://visualdataweb.de/webvowl/#iri=http://purl.org/kao#
- Usage of the Oops tool to improve the ontology design: http://oops.linkeddata.es/response.jsp?uri=http://purl.org/kao#
- Usage of the Vapour tool to improve deferencing URI and content negotiation: http://linkeddata.uriburner.com:8000/vapour?uri=http://purl.org/kao#
Table from SemWeb Best Practices for Dummies with PerfectO applied to the kao ontology (July 2018):
References
Sheth, A., Jaimini, U., Thirunarayan, K., Banerjee, T.: Augmented personalized health: How smart data with iots and ai is about to change healthcare. In: IEEE RTSI. (2017)
Jaimini, U., Banerjee, T., Romine, W., Thirunarayan, K., Sheth, A., Kalra, M.: Investigation of an indoor air quality sensor for asthma management in children. IEEE sensors letters (2017)
Anantharam, P., Banerjee, T., Sheth, A., Thirunarayan, K., Marupudi, S., Sridharan, V., Forbis, S.G.: Knowledge-driven personalized contextual mhealth service for asthma management in children. In: IEEE ICMS. (2015)
Sheth, A., Anantharam, P., Thirunarayan, K.: khealth: Proactive personalized actionable information for better healthcare. In: PDA@ IOT at VLDB. (2014)
Sheth, A., Anantharam, P., Henson, C.: Physical-cyber-social computing: An early 21st century approach. IEEE Intelligent Systems (2013)
Staroch, P.: A weather ontology for predictive control in smart homes. Master’s thesis (2013)
Kofler, M., Reinisch, C., Kastner, W.: An intelligent knowledge representation of smart home energy parameters. In: Proceedings of the World Renewable Energy Congress (WREC). (2011)
Acknowledgments
This work is partially funded by KHealth NIH 1 R01 HD087132-01. The opinions expressed are those of the authors and do not reflect those of the sponsors.